Preface ...................................................... XXIX
List of Contributors ......................................... XXXI
1 Introduction ................................................. 1
Sushil K. Misra
1.1 Introduction to EPR ..................................... 1
1.2 Historical Background of EPR ............................ 2
1.3 Typical X-Band, Low-, and High-Frequency
Spectrometers ........................................... 3
1.4 Applications of EPR .................................... 15
1.5 Scope of This Book ..................................... 20
Acknowledgments ............................................. 21
Further Reading ............................................. 21
2 Multifrequency Aspects of EPR ............................... 23
Sushil K. Misra
2.1 Frequency Bands ........................................ 23
2.2 X-Band EPR ............................................. 23
2.3 EPR at Higher Frequencies (HF) ......................... 24
2.4 Low-Frequency EPR ...................................... 34
2.5 Multifrequency EPR ..................................... 39
Acknowledgments ............................................. 53
Pertinent Literature ........................................ 53
References .................................................. 54
3 Basic Theory of Electron Paramagnetic Resonance ............. 57
Sushil K. Misra
3.1 Introduction ........................................... 57
3.2 Crystal-Field Theory ................................... 58
3.3 Superposition Model (SPM) .............................. 83
3.4 Molecular Orbital (MO) Approach ........................ 85
3.5 The Jahn-Teller (jT) Effect ............................ 92
3.6 The Spin Hamiltonian .................................. 102
3.7 Concluding Remarks .................................... 111
Acknowledgments ............................................ 111
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 111
References ................................................. 111
Part One Experimental ........................................ 115
4 Spectrometers .............................................. 117
4.1 Zero-Field EPR ........................................ 117
Sushil K. Misra
4.2 Low-Frequency CW-EPR Spectrometers: 10MHz to 100GHz ... 128
Harvey A. Buckmaster
4.3 High-Frequency EPR Spectrometers ...................... 175
Edward Reijerse
4.4 Pulsed Techniques in EPR .............................. 290
Sankaran Subramanian and Murali C. Krishna
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 224
References ................................................. 225
5 Multifrequency EPR: Experimental Considerations ............ 229
5.1 Multiarm EPR Spectroscopy at Multiple Microwave
Frequencies: Multiquantum (MQ) EPR, MQ-ELDOR,
Saturation Recovery (SR) EPR, and SR-ELDOR ............ 229
James S. Hyde, Robert A. Strangeway, and Theodore
G. Camenisch
5.2 Resonators for Multifrequency EPR of Spin Labels ...... 244
James S. Hyde, Jason W. Sidabras, Richard R. Mett
Acknowledgments ............................................ 269
References ................................................. 269
5.3 Multifrequency EPR Sensitivity ........................ 270
George A. Rinard, Richard W. Quine, Sandra S. Eaton,
and Gareth R. Eaton
Acknowledgments ............................................ 292
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 292
References ................................................. 292
Part Two Theoretical ......................................... 295
6 First Principles Approach to Spin-Hamiltonian Parameters ... 297
Frank Neese
6.1 Introduction .......................................... 297
6.2 The Spin Hamiltonian .................................. 298
6.3 Electronic Structure Theory of Spin-Hamiltonian
Parameters ............................................ 300
6.4 Concluding Remarks .................................... 323
Acknowledgments ............................................ 324
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 325
References ................................................. 325
7 Spin Hamiltonians and Site Symmetries for Transition
Ions ....................................................... 327
Sushil K. Misra
7.1 Introduction .......................................... 327
7.2 Spin Hamiltonians ..................................... 328
7.3 Spin-Hamiltonian Terms for Various Site Symmetries .... 332
7.4 Transition Ions ....................................... 333
7.5 Concluding Remarks .................................... 363
Acknowledgments ............................................ 363
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 363
References ................................................. 363
Appendix 7.I Spin Operators and Their Matrix Elements .... 365
Appendix 7.II Descent of Symmetry ......................... 381
Appendix 7.III Site Symmetries of Host Crystals ............ 382
8 Evaluation of Spin-Hamiltonian Parameters from
Multifrequency EPR Data .................................... 385
Sushil K. Misra
8.1 Introduction .......................................... 385
8.2 Perturbation Approach ................................. 386
8.3 Brute-Force Methods to Evaluate SHP ................... 394
8.4 Least-Squares Fitting (LSF) Method .................... 395
8.5 Other Applications of the LSF Method .................. 401
8.6 Concluding Remarks .................................... 408
Acknowledgments ............................................ 410
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 420
References ................................................. 420
Appendix 8.1 Historical Review ............................ 422
9 Simulation of EPR Spectra .................................. 427
Sushil K. Misra
9.1 Introduction .......................................... 417
9.2 Simulation of Single-Crystal Spectrum ................. 417
9.3 Simulation of a Polycrystalline Spectrum .............. 421
9.4 Evaluation of Spin-Hamiltonian (SH) Parameters and
the Linewidth from a Polycrystalline EPR Spectrum ..... 429
9.5 Simulation of EPR Spectra in Disordered Materials:
Application to Glassy Materials ....................... 437
9.6 Simulation of EPR Spectra in Disordered Random
Network Materials ..................................... 448
Acknowledgments ............................................ 451
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 451
References ................................................. 452
Appendix 9.1 The Eigenfield Equation ....................... 453
10 Relaxation of Paramagnetic Spins ........................... 455
Sushil K. Misra
10.1 Introduction .......................................... 455
10.2 Equilibrium Magnetization of a Paramagnetic Spin
System ................................................ 457
10.3 Relaxation Phenomena: Spin-Lattice and Spin-Spin
Relaxation Times ...................................... 458
10.4 Rotating Frame ........................................ 459
10.5 Experimental Techniques to Measure Relaxation Times ... 460
10.6 Relaxation Mechanisms ................................. 468
Pertinent literature ....................................... 490
Acknowledgments ............................................ 491
References ................................................. 491
Appendix 10.1 Early History of Paramagnetic Spin-Lattice
Relaxation ................................................. 494
11 Molecular Motions .......................................... 497
Sushil K. Misra and Jack H. Freed
11.1 Introduction .......................................... 497
11.2 Historical Background ................................. 498
11.3 High-Field Multifrequency CW-EPR Experiments to
Unravel Molecular Motion .............................. 500
11.4 Pulsed EPR Study of Molecular Motion .................. 514
11.5 Simulation of Multifrequency EPR Spectra Using More
Atomistic Detail Including Molecular Dynamics and
Stochastic Trajectories ............................... 522
11.6 Concluding Remarks .................................... 541
Acknowledgments ............................................ 541
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 541
References ................................................. 542
12 Distance Measurements: Continuous-Wave (CW)- and Pulsed
Dipolar EPR ................................................ 545
Sushil K. Misra and Jack H. Freed
12.1 Introduction .......................................... 545
12.2 The Dipolar Interaction and Distance Measurements ..... 547
12.3 CW EPR Method to Measure Distances .................... 548
12.4 Pulsed Dipolar EPR Spectroscopy (PDS) ................. 549
12.5 Double Electron-Electron Resonance (DEER) ............. 550
12.6 Six-Pulse DQC ......................................... 559
12.7 Sensitivity Considerations: Multifrequency Aspects .... 570
12.8 Distance Distributions: Tikhonov Regularization ....... 573
12.9 Additional Technical Aspects of DEER and DQC .......... 574
12.10 Concluding Remarks ................................... 576
Acknowledgments ............................................ 576
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 576
References ................................................. 576
Appendix 12.1 Density-Matrix Derivation of Echo Signal
for Three-Pulse DEER .................................... 578
Appendix 12.II Density-Matrix Derivation of the Echo
Signal for Four-Pulse DEER .............................. 582
Appendix 12.III Spin Hamiltonian for Coupled Nitroxides
Used in Six-Pulse DQC Calculation ....................... 584
Appendix 12.IV Algorithm to Calculate Six-Pulse DQC
Signal .................................................. 586
Appendix 12.V Approximate Analytic Expressions for 1-D
DQC Signal .............................................. 587
Part Three Applications ...................................... 589
13 Determination of Large Zero-Field Splitting ................ 591
Sushil K. Misra
13.1 Introduction .......................................... 591
13.2 ZFS of Kramers and Non-Kramers Ions in Different
Environments .......................................... 592
13.3 Concluding Remarks .................................... 596
Acknowledgments ............................................ 597
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 597
References ................................................. 597
14 Determination of Non-Coincident Anisotropic 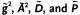 Tensors: Low-Symmetry Considerations ....................... 599
Sushil K. Misra
14.1 Introduction .......................................... 599
14.2 Spin Hamiltonian ...................................... 599
14.3 Eigenvalues ........................................... 601
14.4 Evaluation of SHPs by the LSF Technique ............... 606
14.5 Numerical Evaluation of the Derivatives Required in
the LSF Procedure ..................................... 614
14.6 General Remarks ....................................... 626
Acknowledgments ............................................ 628
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 628
References ................................................. 628
15 Biological Systems ......................................... 629
Boris Dzikovski
15.1 Introduction .......................................... 619
15.2 VHF EPR as the g-Resolved EPR Spectroscopy ............ 620
15.3 Effect of Polarity of the Environment on the
g-Factor .............................................. 623
15.4 Improvement in Orientational Resolution for Spin
Labels ................................................ 628
15.5 Simulation of EPR Spectra at Various Frequencies:
Simple Limiting Cases ................................. 630
15.6 Macroscopically Aligned Phospholipid Membranes ........ 631
15.7 Metalloproteins ....................................... 636
15.8 Concluding Remarks .................................... 641
Acknowledgments ............................................ 642
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 642
References ................................................. 643
16 Copper Coordination Environments ........................... 647
William E. Antholine, Brian Bennett, and Graeme R. Hanson
16.1 Introduction .......................................... 647
16.2 Multifrequency EPR Toolkit ............................ 649
16.3 Multifrequency EPR Simulation of Square-Planar-Based
Cu(II) ................................................ 660
16.4 Copper-Coordination Environments: Multifrequency
EPR of Three-Coordinate Copper and Mixed-Valence
Dinuclear Copper [Cu(1.5+) Cu(1.5+)] .................. 677
16.5 Structural Characterization of Copper(II) Cyclic
Peptide Complexes Employing Multifrequency EPR and
Computational Chemistry ............................... 699
16.6 Summary ............................................... 711
Acknowledgments ............................................ 711
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 712
Section 16.3 ............................................... 712
Section 16.4 ............................................... 713
References ................................................. 714
17 Multifrequency Electron Spin-Relaxation Times .............. 729
Careth R. Eaton and Sandra S. Eaton
17.1 Introduction and Scope of the Chapter ................. 729
17.2 Spin-Spin Relaxation, T2 and Tm ....................... 720
17.3 Spin-lattice Relaxation, T1 ........................... 726
Acknowledgments ............................................ 748
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 748
References ................................................. 748
18 EPR Imaging: Theory and Instrumentation .................... 755
Rizwan Ahmad and Periannan Kuppusamy
18.1 Introduction .......................................... 755
18.2 EPR Principle: Zeeman Effect .......................... 756
18.3 CW-EPR Imager ......................................... 760
18.4 Data Acquisition for CW-EPR and EPRI .................. 769
18.5 Important Imaging Parameters .......................... 774
18.6 Image Reconstruction .................................. 776
18.7 Other Data Collection Modalities ...................... 783
18.8 Constraints for Biological Applications ............... 785
18.9 Special Imaging Applications .......................... 786
18.10 Scope and Limitations ................................ 790
Acknowledgments ............................................ 791
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 792
References ................................................. 792
19 Multifrequency EPR Microscopy: Experimental and
Theoretical Aspects ........................................ 795
Aharon Blank
19.1 General ............................................... 795
19.2 Introduction .......................................... 795
19.3 General Experimental Aspects of EPR Microscopy ........ 798
19.4 Specific Aspects of Multifrequency EPR Microscopy at
Various Temperatures .................................. 811
19.5 Illustrative Examples ................................. 815
19.6 Conclusions and Future Prospects ...................... 821
Acknowledgments ............................................ 821
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 821
References ................................................. 822
20 EPR Studies of Nanomaterials ............................... 825
Alex Smirnov
20.1 Introduction .......................................... 825
20.2 EPR Studies of Magnetic Nanostructures ................ 827
20.3 Characterization of Nanostructured Oxide
Semiconductors for Photoactivated Catalysis and
Solar Energy Conversion ............................... 832
20.4 Surface Radicals, Catalytic Activity, Cytotoxicity,
and Radical-Scavenging Properties of Nanomaterials .... 833
20.5 Spin-Labeling EPR Studies of Ligand-Protected
Nanoparticles and Hybrid Nanostructures ............... 835
20.6 Summary and Future Perspectives ....................... 841
Acknowledgments ............................................ 842
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 842
References ................................................. 842
21 Single-Molecule Magnets and Magnetic Quantum Tunneling ..... 845
Sushil K. Misra
21.1 Introduction .......................................... 845
21.2 Multifrequency EPR of SMMs: Magnetic Hysteresis and
MQT ................................................... 852
21.3 Magnetic Quantum Tunneling (MQT): Pure and Thermally
Assisted Tunneling .................................... 867
21.4 Concluding Remarks .................................... 872
Acknowledgments ............................................ 872
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 872
References ................................................. 872
22 Multifrequency EPR on Photosynthetic Systems ............... 875
Sushil K. Misra, Klaus Möbius, and Anton Savitsky
22.1 Introduction .......................................... 875
22.2 Nonoxygenic Photosynthesis ............................ 880
22.3 Multifrequency EPR on Bacterial Photosynthetic
Reaction Centers (RCs) ................................ 882
22.4 Oxygenic Photosynthesis ............................... 897
22.5 Concluding Remarks .................................... 902
Acknowledgments ............................................ 904
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 904
References ................................................. 905
23 Measurement of Superconducting Caps ........................ 913
Sushil K. Misra
23.1 Introduction .......................................... 913
23.2 The Superconducting Gap ............................... 913
23.3 Measurement of SCG .................................... 914
23.4 Concluding Remarks .................................... 917
Acknowledgments ............................................ 918
References ................................................. 919
24 Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) at High Magnetic
Fields ..................................................... 922
Thomas Prisner and Mark J. Prandolini
24.1 Introduction .......................................... 921
24.2 Historical Aspects (Metals, Solids and Liquids) at
Lower Magnetic Fields ................................. 922
24.3 Theory ................................................ 924
24.4 Hardware (High-Frequency Microwave Equipment, SS-MAS
DNP, HF-Liquid DNP, Dissolution DNP, Shuttle-DNP) ..... 936
24.5 First Applications and Outlook ........................ 942
25 Chemically Induced Electron and Nuclear Polarization ....... 947
Lawrence J. Berliner and Elena Bagryanskaya
25.1 Introduction .......................................... 947
25.2 History of the CIDNP Phenomenon ....................... 948
25.3 The Radical Pair Mechanism ............................ 948
25.4 Chemically Induced Dynamic Nuclear Polarization ....... 952
25.5 Chemically Induced Dynamic Electron Polarization ...... 967
25.6 Conclusion ............................................ 984
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 986
References ................................................. 988
Part Four Future Perspectives ................................ 993
26 Future Perspectives ........................................ 995
Sushil K. Misra
26.1 Spectroscopic Techniques Currently Available in EPR ... 995
26.2 Cutting-Edge Topics ................................... 999
26.3 Desirable Applications of EPR ........................ 1003
26.4 Future of EPR ........................................ 1003
Acknowledgments ........................................... 1004
Appendix Al Fundamental Constants and Conversion Factors
used in EPR ............................................... 1005
Index ........................................................ 1009
Tensors: Low-Symmetry Considerations ....................... 599
Sushil K. Misra
14.1 Introduction .......................................... 599
14.2 Spin Hamiltonian ...................................... 599
14.3 Eigenvalues ........................................... 601
14.4 Evaluation of SHPs by the LSF Technique ............... 606
14.5 Numerical Evaluation of the Derivatives Required in
the LSF Procedure ..................................... 614
14.6 General Remarks ....................................... 626
Acknowledgments ............................................ 628
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 628
References ................................................. 628
15 Biological Systems ......................................... 629
Boris Dzikovski
15.1 Introduction .......................................... 619
15.2 VHF EPR as the g-Resolved EPR Spectroscopy ............ 620
15.3 Effect of Polarity of the Environment on the
g-Factor .............................................. 623
15.4 Improvement in Orientational Resolution for Spin
Labels ................................................ 628
15.5 Simulation of EPR Spectra at Various Frequencies:
Simple Limiting Cases ................................. 630
15.6 Macroscopically Aligned Phospholipid Membranes ........ 631
15.7 Metalloproteins ....................................... 636
15.8 Concluding Remarks .................................... 641
Acknowledgments ............................................ 642
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 642
References ................................................. 643
16 Copper Coordination Environments ........................... 647
William E. Antholine, Brian Bennett, and Graeme R. Hanson
16.1 Introduction .......................................... 647
16.2 Multifrequency EPR Toolkit ............................ 649
16.3 Multifrequency EPR Simulation of Square-Planar-Based
Cu(II) ................................................ 660
16.4 Copper-Coordination Environments: Multifrequency
EPR of Three-Coordinate Copper and Mixed-Valence
Dinuclear Copper [Cu(1.5+) Cu(1.5+)] .................. 677
16.5 Structural Characterization of Copper(II) Cyclic
Peptide Complexes Employing Multifrequency EPR and
Computational Chemistry ............................... 699
16.6 Summary ............................................... 711
Acknowledgments ............................................ 711
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 712
Section 16.3 ............................................... 712
Section 16.4 ............................................... 713
References ................................................. 714
17 Multifrequency Electron Spin-Relaxation Times .............. 729
Careth R. Eaton and Sandra S. Eaton
17.1 Introduction and Scope of the Chapter ................. 729
17.2 Spin-Spin Relaxation, T2 and Tm ....................... 720
17.3 Spin-lattice Relaxation, T1 ........................... 726
Acknowledgments ............................................ 748
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 748
References ................................................. 748
18 EPR Imaging: Theory and Instrumentation .................... 755
Rizwan Ahmad and Periannan Kuppusamy
18.1 Introduction .......................................... 755
18.2 EPR Principle: Zeeman Effect .......................... 756
18.3 CW-EPR Imager ......................................... 760
18.4 Data Acquisition for CW-EPR and EPRI .................. 769
18.5 Important Imaging Parameters .......................... 774
18.6 Image Reconstruction .................................. 776
18.7 Other Data Collection Modalities ...................... 783
18.8 Constraints for Biological Applications ............... 785
18.9 Special Imaging Applications .......................... 786
18.10 Scope and Limitations ................................ 790
Acknowledgments ............................................ 791
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 792
References ................................................. 792
19 Multifrequency EPR Microscopy: Experimental and
Theoretical Aspects ........................................ 795
Aharon Blank
19.1 General ............................................... 795
19.2 Introduction .......................................... 795
19.3 General Experimental Aspects of EPR Microscopy ........ 798
19.4 Specific Aspects of Multifrequency EPR Microscopy at
Various Temperatures .................................. 811
19.5 Illustrative Examples ................................. 815
19.6 Conclusions and Future Prospects ...................... 821
Acknowledgments ............................................ 821
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 821
References ................................................. 822
20 EPR Studies of Nanomaterials ............................... 825
Alex Smirnov
20.1 Introduction .......................................... 825
20.2 EPR Studies of Magnetic Nanostructures ................ 827
20.3 Characterization of Nanostructured Oxide
Semiconductors for Photoactivated Catalysis and
Solar Energy Conversion ............................... 832
20.4 Surface Radicals, Catalytic Activity, Cytotoxicity,
and Radical-Scavenging Properties of Nanomaterials .... 833
20.5 Spin-Labeling EPR Studies of Ligand-Protected
Nanoparticles and Hybrid Nanostructures ............... 835
20.6 Summary and Future Perspectives ....................... 841
Acknowledgments ............................................ 842
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 842
References ................................................. 842
21 Single-Molecule Magnets and Magnetic Quantum Tunneling ..... 845
Sushil K. Misra
21.1 Introduction .......................................... 845
21.2 Multifrequency EPR of SMMs: Magnetic Hysteresis and
MQT ................................................... 852
21.3 Magnetic Quantum Tunneling (MQT): Pure and Thermally
Assisted Tunneling .................................... 867
21.4 Concluding Remarks .................................... 872
Acknowledgments ............................................ 872
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 872
References ................................................. 872
22 Multifrequency EPR on Photosynthetic Systems ............... 875
Sushil K. Misra, Klaus Möbius, and Anton Savitsky
22.1 Introduction .......................................... 875
22.2 Nonoxygenic Photosynthesis ............................ 880
22.3 Multifrequency EPR on Bacterial Photosynthetic
Reaction Centers (RCs) ................................ 882
22.4 Oxygenic Photosynthesis ............................... 897
22.5 Concluding Remarks .................................... 902
Acknowledgments ............................................ 904
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 904
References ................................................. 905
23 Measurement of Superconducting Caps ........................ 913
Sushil K. Misra
23.1 Introduction .......................................... 913
23.2 The Superconducting Gap ............................... 913
23.3 Measurement of SCG .................................... 914
23.4 Concluding Remarks .................................... 917
Acknowledgments ............................................ 918
References ................................................. 919
24 Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) at High Magnetic
Fields ..................................................... 922
Thomas Prisner and Mark J. Prandolini
24.1 Introduction .......................................... 921
24.2 Historical Aspects (Metals, Solids and Liquids) at
Lower Magnetic Fields ................................. 922
24.3 Theory ................................................ 924
24.4 Hardware (High-Frequency Microwave Equipment, SS-MAS
DNP, HF-Liquid DNP, Dissolution DNP, Shuttle-DNP) ..... 936
24.5 First Applications and Outlook ........................ 942
25 Chemically Induced Electron and Nuclear Polarization ....... 947
Lawrence J. Berliner and Elena Bagryanskaya
25.1 Introduction .......................................... 947
25.2 History of the CIDNP Phenomenon ....................... 948
25.3 The Radical Pair Mechanism ............................ 948
25.4 Chemically Induced Dynamic Nuclear Polarization ....... 952
25.5 Chemically Induced Dynamic Electron Polarization ...... 967
25.6 Conclusion ............................................ 984
Pertinent Literature ....................................... 986
References ................................................. 988
Part Four Future Perspectives ................................ 993
26 Future Perspectives ........................................ 995
Sushil K. Misra
26.1 Spectroscopic Techniques Currently Available in EPR ... 995
26.2 Cutting-Edge Topics ................................... 999
26.3 Desirable Applications of EPR ........................ 1003
26.4 Future of EPR ........................................ 1003
Acknowledgments ........................................... 1004
Appendix Al Fundamental Constants and Conversion Factors
used in EPR ............................................... 1005
Index ........................................................ 1009
|