Foreword ..................................................... xiii
Preface ........................................................ xv
Description of the book ..................................... xv
Prologue ...................................................... xxi
Some notation .............................................. xxi
The space 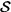 ( (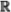 n) and its dual n) and its dual 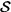 '( '(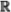 n) ..................... xxii
The Fourier transform .................................... xxiii
Part I Symplectic Mechanics
1 Hamiltonian Mechanics in a Nutshell
1.1 Hamilton's equations .................................... 3
1.1.1 Definition of Hamiltonian systems ................ 3
1.1.2 A simple existence and uniqueness result ......... 4
1.2 Hamiltonian fields and flows ............................ 6
1.2.1 The Hamilton vector field ........................ 6
1.2.2 The symplectic character of Hamiltonian flows .... 8
1.2.3 Poisson brackets ................................ 10
1.3 Additional topics ...................................... 11
1.3.1 Hamilton-Jacobi theory .......................... 11
1.3.2 The invariant volume form ....................... 13
1.3.3 The problem of "Quantization" ................... 16
2 The Symplectic Group
2.1 Symplectic matrices .................................... 20
2.1.1 Definition of the symplectic group .............. 20
2.1.2 Symplectic block-matrices ....................... 20
2.1.3 The affine symplectic group ..................... 21
2.2 Symplectic forms ....................................... 22
2.2.1 The notion of symplectic form .................. 22
2.2.2 Differential formulation ........................ 23
2.3 The unitary groups U(n, n) ..................... xxii
The Fourier transform .................................... xxiii
Part I Symplectic Mechanics
1 Hamiltonian Mechanics in a Nutshell
1.1 Hamilton's equations .................................... 3
1.1.1 Definition of Hamiltonian systems ................ 3
1.1.2 A simple existence and uniqueness result ......... 4
1.2 Hamiltonian fields and flows ............................ 6
1.2.1 The Hamilton vector field ........................ 6
1.2.2 The symplectic character of Hamiltonian flows .... 8
1.2.3 Poisson brackets ................................ 10
1.3 Additional topics ...................................... 11
1.3.1 Hamilton-Jacobi theory .......................... 11
1.3.2 The invariant volume form ....................... 13
1.3.3 The problem of "Quantization" ................... 16
2 The Symplectic Group
2.1 Symplectic matrices .................................... 20
2.1.1 Definition of the symplectic group .............. 20
2.1.2 Symplectic block-matrices ....................... 20
2.1.3 The affine symplectic group ..................... 21
2.2 Symplectic forms ....................................... 22
2.2.1 The notion of symplectic form .................. 22
2.2.2 Differential formulation ........................ 23
2.3 The unitary groups U(n, 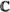 ) and U(2n, ) and U(2n, 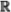 ) ............... 25
2.3.1 A useful monomorphism ........................... 25
2.3.2 Symplectic rotations ............................ 25
2.3.3 Diagonalization and polar decomposition ......... 26
2.4 Symplectic bases and Lagrangian planes ................. 28
2.4.1 Definition of a symplectic basis ................ 28
2.4.2 The Lagrangian Grassmannian ..................... 29
3 Free Symplectic Matrices
3.1 Generating functions ................................... 31
3.1.1 Definition of a free symplectic matrix .......... 31
3.1.2 The notion of generating function ............... 33
3.1.3 Application to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation ..... 35
3.2 A factorization result ................................. 38
3.2.1 Statement and proof ............................. 38
3.2.2 Application: generators of Sp(2n, ) ............... 25
2.3.1 A useful monomorphism ........................... 25
2.3.2 Symplectic rotations ............................ 25
2.3.3 Diagonalization and polar decomposition ......... 26
2.4 Symplectic bases and Lagrangian planes ................. 28
2.4.1 Definition of a symplectic basis ................ 28
2.4.2 The Lagrangian Grassmannian ..................... 29
3 Free Symplectic Matrices
3.1 Generating functions ................................... 31
3.1.1 Definition of a free symplectic matrix .......... 31
3.1.2 The notion of generating function ............... 33
3.1.3 Application to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation ..... 35
3.2 A factorization result ................................. 38
3.2.1 Statement and proof ............................. 38
3.2.2 Application: generators of Sp(2n, 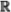 ) ........... 39
4 The Group of Hamiltonian Symplectomorphisms
4.1 The group Symp(2n, ) ........... 39
4 The Group of Hamiltonian Symplectomorphisms
4.1 The group Symp(2n, 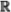 ) ................................. 41
4.1.1 Definition and examples ......................... 41
4.2 Hamiltonian symplectomorphisms ......................... 43
4.2.1 Symplectic covariance of Hamiltonian flows ...... 43
4.2.2 The group Ham(2n, ) ................................. 41
4.1.1 Definition and examples ......................... 41
4.2 Hamiltonian symplectomorphisms ......................... 43
4.2.1 Symplectic covariance of Hamiltonian flows ...... 43
4.2.2 The group Ham(2n, 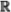 ) ........................... 44
4.3 The symplectic Lie algebra ............................. 47
4.3.1 Matrix characterization of sp(2n, ) ........................... 44
4.3 The symplectic Lie algebra ............................. 47
4.3.1 Matrix characterization of sp(2n, 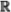 ) ........... 48
4.3.2 The exponential mapping ......................... 49
5 Symplectic Capacities
5.1 Gromov's theorem and symplectic capacities ............. 51
5.1.1 Statement of Gromov's theorem ................... 51
5.1.2 Proof of Gromov's theorem in the affine case .... 52
5.2 The notion of symplectic capacity ...................... 55
5.2.1 Definition and existence ........................ 55
5.2.2 The symplectic capacity of an ellipsoid ......... 59
5.3 Other symplectic capacities ............................ 61
5.3.1 The Hofer-Zehnder capacity ...................... 61
5.3.2 The Ekeland-Hofer capacities .................... 62
6 Uncertainty Principles
6.1 The Robertson-Schrodinger inequalities ................. 66
6.1.1 The covariance matrix ........................... 66
6.1.2 A strong version of the Robertson-Schrodinger
uncertainty principle ........................... 67
6.1.3 Symplectic capacity and the strong
uncertainty principle ........................... 70
6.2 Hardy's uncertainty principle .......................... 71
6.2.1 Two useful lemmas ............................... 72
6.2.2 Proof of the multi-dimensional Hardy
uncertainty principle ........................... 74
6.2.3 Geometric interpretation ........................ 76
Part II Harmonic Analysis in Symplectic Spaces
7 The Metaplectic Group
7.1 The metaplectic representation ......................... 79
7.1.1 A preliminary remark, and a caveat .............. 80
7.1.2 Quadratic Fourier transforms .................... 80
7.2 The projection ) ........... 48
4.3.2 The exponential mapping ......................... 49
5 Symplectic Capacities
5.1 Gromov's theorem and symplectic capacities ............. 51
5.1.1 Statement of Gromov's theorem ................... 51
5.1.2 Proof of Gromov's theorem in the affine case .... 52
5.2 The notion of symplectic capacity ...................... 55
5.2.1 Definition and existence ........................ 55
5.2.2 The symplectic capacity of an ellipsoid ......... 59
5.3 Other symplectic capacities ............................ 61
5.3.1 The Hofer-Zehnder capacity ...................... 61
5.3.2 The Ekeland-Hofer capacities .................... 62
6 Uncertainty Principles
6.1 The Robertson-Schrodinger inequalities ................. 66
6.1.1 The covariance matrix ........................... 66
6.1.2 A strong version of the Robertson-Schrodinger
uncertainty principle ........................... 67
6.1.3 Symplectic capacity and the strong
uncertainty principle ........................... 70
6.2 Hardy's uncertainty principle .......................... 71
6.2.1 Two useful lemmas ............................... 72
6.2.2 Proof of the multi-dimensional Hardy
uncertainty principle ........................... 74
6.2.3 Geometric interpretation ........................ 76
Part II Harmonic Analysis in Symplectic Spaces
7 The Metaplectic Group
7.1 The metaplectic representation ......................... 79
7.1.1 A preliminary remark, and a caveat .............. 80
7.1.2 Quadratic Fourier transforms .................... 80
7.2 The projection  Мр ..................................... 84
7.2.1 Precise statement ............................... 84
7.2.2 Dependence on ħ ................................. 85
7.3 Construction of Мр ..................................... 84
7.2.1 Precise statement ............................... 84
7.2.2 Dependence on ħ ................................. 85
7.3 Construction of  Мр .................................... 87
7.3.1 The group Diff(1)(n) ............................. 87
7.3.2 Construction of the projection .................. 89
8 Heisenberg-Weyl and Grossmann-Royer Operators
8.1 Dynamical motivation, and definition ................... 91
8.1.1 The displacement Hamiltonian .................... 91
8.1.2 The Heisenberg-Weyl operators ................... 93
8.1.3 The symplectic covariance property of the HW
operators ....................................... 95
8.2 The Heisenberg group ................................... 96
8.2.1 The canonical commutation relations ............. 97
8.2.2 Heisenberg group and Schrodinger
representation .................................. 98
8.2.3 The Stone-von Neumann theorem .................. 100
8.3 The Grossmann-Royer operators ......................... 102
8.3.1 The symplectic Fourier transform ............... 102
8.3.2 Definition of the Grossmann-Royer operators .... 104
8.3.3 Symplectic covariance .......................... 106
8.4 Weyl-Heisenberg frames ................................ 107
8.4.1 The notion of frame ............................ 108
8.4.2 Weyl-Heisenberg frames ......................... 111
8.4.3 A useful "dictionary" .......................... 113
9 Cross-ambiguity and Wigner Functions
9.1 The cross-ambiguity function .......................... 117
9.1.1 Definition of А(ψ, ϕ) .......................... 117
9.1.2 Elementary properties of the cross-ambiguity
function ....................................... 119
9.2 The cross-Wigner transform ............................ 120
9.2.1 Definition and first properties of W(ψ, ϕ) ..... 120
9.2.2 Translations of Wigner transforms .............. 122
9.3 Relations between А(ψ, ϕ), W(ψ, ϕ), and the STFT ...... 123
9.3.1 Two simple formulas ............................ 123
9.3.2 The short-time Fourier transform ............... 125
9.3.3 The Cohen class ................................ 126
9.4 The Moyal identity .................................... 128
9.4.1 Statement and proof ............................ 128
9.4.2 An inversion formula ........................... 130
9.5 Continuity and growth properties ...................... 132
9.5.1 Continuity of А(ψ, ϕ) and W(ψ, ϕ) .............. 132
9.5.2 Decay properties of А(ψ, ϕ) and W(ψ, ϕ) ........ 134
10 The Weyl Correspondence
10.1 The Weyl correspondence ............................... 137
10.1.1 First definitions and properties ............... 137
10.1.2 Definition using the Wigner transform .......... 140
10.1.3 Probabilistic interpretation ................... 142
10.1.4 The kernel of a Weyl operator .................. 144
10.2 Adjoints and products ................................. 146
10.2.1 The adjoint of a Weyl operator ................. 146
10.2.2 Composition formulas ........................... 147
10.3 Symplectic covariance of Weyl operators ............... 150
10.3.1 Statement and proof of the symplectic
covariance property ............................ 150
10.3.2 Covariance under affine symplectomorphisms ..... 151
10.4 Weyl operators as pseudo-differential operators ....... 152
10.4.1 The notion of pseudo-differential operator ..... 153
10.4.2 The kernel of a Weyl operator revisited ........ 155
10.4.3 Justification in the case α Мр .................................... 87
7.3.1 The group Diff(1)(n) ............................. 87
7.3.2 Construction of the projection .................. 89
8 Heisenberg-Weyl and Grossmann-Royer Operators
8.1 Dynamical motivation, and definition ................... 91
8.1.1 The displacement Hamiltonian .................... 91
8.1.2 The Heisenberg-Weyl operators ................... 93
8.1.3 The symplectic covariance property of the HW
operators ....................................... 95
8.2 The Heisenberg group ................................... 96
8.2.1 The canonical commutation relations ............. 97
8.2.2 Heisenberg group and Schrodinger
representation .................................. 98
8.2.3 The Stone-von Neumann theorem .................. 100
8.3 The Grossmann-Royer operators ......................... 102
8.3.1 The symplectic Fourier transform ............... 102
8.3.2 Definition of the Grossmann-Royer operators .... 104
8.3.3 Symplectic covariance .......................... 106
8.4 Weyl-Heisenberg frames ................................ 107
8.4.1 The notion of frame ............................ 108
8.4.2 Weyl-Heisenberg frames ......................... 111
8.4.3 A useful "dictionary" .......................... 113
9 Cross-ambiguity and Wigner Functions
9.1 The cross-ambiguity function .......................... 117
9.1.1 Definition of А(ψ, ϕ) .......................... 117
9.1.2 Elementary properties of the cross-ambiguity
function ....................................... 119
9.2 The cross-Wigner transform ............................ 120
9.2.1 Definition and first properties of W(ψ, ϕ) ..... 120
9.2.2 Translations of Wigner transforms .............. 122
9.3 Relations between А(ψ, ϕ), W(ψ, ϕ), and the STFT ...... 123
9.3.1 Two simple formulas ............................ 123
9.3.2 The short-time Fourier transform ............... 125
9.3.3 The Cohen class ................................ 126
9.4 The Moyal identity .................................... 128
9.4.1 Statement and proof ............................ 128
9.4.2 An inversion formula ........................... 130
9.5 Continuity and growth properties ...................... 132
9.5.1 Continuity of А(ψ, ϕ) and W(ψ, ϕ) .............. 132
9.5.2 Decay properties of А(ψ, ϕ) and W(ψ, ϕ) ........ 134
10 The Weyl Correspondence
10.1 The Weyl correspondence ............................... 137
10.1.1 First definitions and properties ............... 137
10.1.2 Definition using the Wigner transform .......... 140
10.1.3 Probabilistic interpretation ................... 142
10.1.4 The kernel of a Weyl operator .................. 144
10.2 Adjoints and products ................................. 146
10.2.1 The adjoint of a Weyl operator ................. 146
10.2.2 Composition formulas ........................... 147
10.3 Symplectic covariance of Weyl operators ............... 150
10.3.1 Statement and proof of the symplectic
covariance property ............................ 150
10.3.2 Covariance under affine symplectomorphisms ..... 151
10.4 Weyl operators as pseudo-differential operators ....... 152
10.4.1 The notion of pseudo-differential operator ..... 153
10.4.2 The kernel of a Weyl operator revisited ........ 155
10.4.3 Justification in the case α 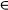 Sm ............... 156
10.5 Regularity results for Weyl operators ................. 158
10.5.1 Some general results ........................... 158
10.5.2 Symbols in Lq spaces ........................... 160
11 Coherent States and Anti-Wick Quantization
11.1 Coherent states ....................................... 163
11.1.1 A physical motivation .......................... 163
11.1.2 Properties of coherent states .................. 164
11.2 Wigner transforms of Gaussians ........................ 169
11.2.1 Some explicit formulas ......................... 169
11.2.2 The cross-Wigner transform of a pair of
Gaussians ...................................... 171
11.3 Squeezed coherent states .............................. 172
11.3.1 Definition and characterization ................ 173
11.3.2 Explicit action of Mp(2n, Sm ............... 156
10.5 Regularity results for Weyl operators ................. 158
10.5.1 Some general results ........................... 158
10.5.2 Symbols in Lq spaces ........................... 160
11 Coherent States and Anti-Wick Quantization
11.1 Coherent states ....................................... 163
11.1.1 A physical motivation .......................... 163
11.1.2 Properties of coherent states .................. 164
11.2 Wigner transforms of Gaussians ........................ 169
11.2.1 Some explicit formulas ......................... 169
11.2.2 The cross-Wigner transform of a pair of
Gaussians ...................................... 171
11.3 Squeezed coherent states .............................. 172
11.3.1 Definition and characterization ................ 173
11.3.2 Explicit action of Mp(2n, 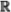 ) on squeezed
states ......................................... 175
11.4 Anti-Wick quantization ................................ 177
11.4.1 Definition in terms of coherent states ......... 178
11.4.2 The Weyl symbol of an anti-Wick operator ....... 180
11.4.3 Some regularity results ........................ 181
12 Hubert-Schmidt and Trace Class Operators
12.1 Hilbert-Schmidt operators ............................. 185
12.1.1 Definition and general properties .............. 185
12.1.2 Hilbert-Schmidt operators on L2( ) on squeezed
states ......................................... 175
11.4 Anti-Wick quantization ................................ 177
11.4.1 Definition in terms of coherent states ......... 178
11.4.2 The Weyl symbol of an anti-Wick operator ....... 180
11.4.3 Some regularity results ........................ 181
12 Hubert-Schmidt and Trace Class Operators
12.1 Hilbert-Schmidt operators ............................. 185
12.1.1 Definition and general properties .............. 185
12.1.2 Hilbert-Schmidt operators on L2(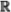 n) ........... 188
12.2 Trace class operators ................................. 189
12.2.1 The trace of a positive operator ............... 189
12.2.2 General trace class operators .................. 193
12.3 The trace of a Weyl operator .......................... 198
12.3.1 Heuristic discussion ........................... 198
12.3.2 Some rigorous results .......................... 200
13 Density Operator and Quantum States
13.1 The density operator .................................. 205
13.1.1 Pure and mixed quantum states .................. 206
13.2 The uncertainty principle revisited ................... 210
13.2.1 The strong uncertainty principle for the
density operator ............................... 210
13.2.2 Sub-Gaussian estimates ......................... 212
13.2.3 Positivity issues and the KLM conditions ....... 215
Part III Pseudo-differential Operators and Function Spaces
14 Shubin's Global Operator Calculus
14.1 The Shubin classes .................................... 223
14.1.1 Generalities ................................... 223
14.1.2 Definitions and preliminary results ............ 225
14.1.3 Asymptotic expansions of symbols ............... 229
14.2 More general operators ... which are not more
general! .............................................. 230
14.2.1 More general classes of symbols ................ 231
14.2.2 A reduction result ............................. 232
14.3 Relations between kernels and symbols ................. 236
14.3.1 A general result ............................... 236
14.3.2 Application: Wigner and Rihaczek
distributions .................................. 237
14.4 Adjoints and products ................................. 239
14.4.1 The transpose and adjoint operators ............ 239
14.4.2 Composition formulas ........................... 240
14.5 Proof of Theorem 330 .................................. 243
Part IV Applications
15 The Schrodinger Equation
15.1 The case of quadratic Hamiltonians .................... 247
15.1.1 Preliminaries .................................. 248
15.1.2 Quadratic Hamiltonians ......................... 249
15.1.3 Exact solutions of the Schrodinger equation .... 252
15.2 The general case ...................................... 254
15.2.1 Symplectic covariance as a characteristic
property of Weyl quantization .................. 254
15.2.2 Quantum evolution groups and Stone's theorem ... 256
15.2.3 Application to Schrodinger's equation .......... 256
16 The Feichtinger Algebra
16.1 Definition and first properties ....................... 261
16.1.1 Definition of n) ........... 188
12.2 Trace class operators ................................. 189
12.2.1 The trace of a positive operator ............... 189
12.2.2 General trace class operators .................. 193
12.3 The trace of a Weyl operator .......................... 198
12.3.1 Heuristic discussion ........................... 198
12.3.2 Some rigorous results .......................... 200
13 Density Operator and Quantum States
13.1 The density operator .................................. 205
13.1.1 Pure and mixed quantum states .................. 206
13.2 The uncertainty principle revisited ................... 210
13.2.1 The strong uncertainty principle for the
density operator ............................... 210
13.2.2 Sub-Gaussian estimates ......................... 212
13.2.3 Positivity issues and the KLM conditions ....... 215
Part III Pseudo-differential Operators and Function Spaces
14 Shubin's Global Operator Calculus
14.1 The Shubin classes .................................... 223
14.1.1 Generalities ................................... 223
14.1.2 Definitions and preliminary results ............ 225
14.1.3 Asymptotic expansions of symbols ............... 229
14.2 More general operators ... which are not more
general! .............................................. 230
14.2.1 More general classes of symbols ................ 231
14.2.2 A reduction result ............................. 232
14.3 Relations between kernels and symbols ................. 236
14.3.1 A general result ............................... 236
14.3.2 Application: Wigner and Rihaczek
distributions .................................. 237
14.4 Adjoints and products ................................. 239
14.4.1 The transpose and adjoint operators ............ 239
14.4.2 Composition formulas ........................... 240
14.5 Proof of Theorem 330 .................................. 243
Part IV Applications
15 The Schrodinger Equation
15.1 The case of quadratic Hamiltonians .................... 247
15.1.1 Preliminaries .................................. 248
15.1.2 Quadratic Hamiltonians ......................... 249
15.1.3 Exact solutions of the Schrodinger equation .... 252
15.2 The general case ...................................... 254
15.2.1 Symplectic covariance as a characteristic
property of Weyl quantization .................. 254
15.2.2 Quantum evolution groups and Stone's theorem ... 256
15.2.3 Application to Schrodinger's equation .......... 256
16 The Feichtinger Algebra
16.1 Definition and first properties ....................... 261
16.1.1 Definition of 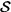 0( 0(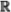 n) .......................... 262
16.1.2 First properties of n) .......................... 262
16.1.2 First properties of 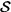 0( 0(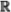 n) .................... 263
16.2 Invariance and Banach algebra properties .............. 266
16.2.1 Metaplectic invariance of the Feichtinger
algebra ........................................ 266
16.2.2 The algebra property of n) .................... 263
16.2 Invariance and Banach algebra properties .............. 266
16.2.1 Metaplectic invariance of the Feichtinger
algebra ........................................ 266
16.2.2 The algebra property of 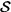 0( 0(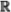 n) ................ 268
16.3 A minimality property for n) ................ 268
16.3 A minimality property for 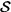 0( 0( n) ..................... 270
16.3.1 Heisenberg-Weyl expansions ..................... 270
16.3.2 The minimality property ........................ 271
16.4 A Banach Gelfand triple ............................... 271
16.4.1 The dual space n) ..................... 270
16.3.1 Heisenberg-Weyl expansions ..................... 270
16.3.2 The minimality property ........................ 271
16.4 A Banach Gelfand triple ............................... 271
16.4.1 The dual space  '0( '0( n) ........................ 272
16.4.2 The Gelfand triple ( n) ........................ 272
16.4.2 The Gelfand triple ( 0, L2, 0, L2, 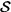 '0) .............. 273
17 The Modulation Spaces Mqs
17.1 The Lq spaces, 1 ≤ q < ∞ .............................. 275
17.1.1 Definitions .................................... 275
17.1.2 Weighted Lq spaces ............................. 278
17.2 The modulation spaces Mqs ............................. 281
17.2.1 Definition of Mqs .............................. 282
17.2.2 Metaplectic and Heisenberg-Weyl invariance
properties ..................................... 284
17.3 The modulation spaces Ms∞ ............................. 285
17.3.1 The weighted spaces Ms∞ ........................ 285
17.3.2 The spaces M∞s ................................. 286
17.4 The modulation spaces Ms∞,1 ........................... 287
17.4.1 Definition and first properties ................ 288
17.4.2 Weyl operators with symbols in Ms∞,1 ........... 290
18 Bopp Pseudo-differential Operators
18.1 Introduction and motivation ........................... 292
18.1.1 Bopp pseudo-differential operators ............. 293
18.1.2 Bopp operators viewed as Weyl operators ........ 295
18.1.3 Adjoints and a composition formula ............. 297
18.1.4 Symplectic covariance of Bopp operators ........ 298
18.2 Intertwiners .......................................... 299
18.2.1 Windowed wavepacket transforms ................. 299
18.2.2 The intertwining property ...................... 302
18.3 Regularity results for Bopp operators ................. 303
18.3.1 Boundedness results ............................ 303
18.3.2 Global hypoellipticity properties .............. 304
19 Applications of Bopp Quantization
19.1 Spectral results for Bopp operators ................... 307
19.1.1 A fundamental property of the intertwiners ..... 307
19.1.2 Generalized eigenvalues and eigenvectors
of a Bopp operator ............................. 309
19.1.3 Application: the Landau problem ................ 312
19.2 Bopp calculus and deformation quantization ............ 314
19.2.1 Deformation quantization: motivation ........... 315
19.2.2 The Moyal product and bracket .................. 316
19.3 Non-commutative quantum mechanics ..................... 318
19.3.1 Background ..................................... 318
19.3.2 The operators '0) .............. 273
17 The Modulation Spaces Mqs
17.1 The Lq spaces, 1 ≤ q < ∞ .............................. 275
17.1.1 Definitions .................................... 275
17.1.2 Weighted Lq spaces ............................. 278
17.2 The modulation spaces Mqs ............................. 281
17.2.1 Definition of Mqs .............................. 282
17.2.2 Metaplectic and Heisenberg-Weyl invariance
properties ..................................... 284
17.3 The modulation spaces Ms∞ ............................. 285
17.3.1 The weighted spaces Ms∞ ........................ 285
17.3.2 The spaces M∞s ................................. 286
17.4 The modulation spaces Ms∞,1 ........................... 287
17.4.1 Definition and first properties ................ 288
17.4.2 Weyl operators with symbols in Ms∞,1 ........... 290
18 Bopp Pseudo-differential Operators
18.1 Introduction and motivation ........................... 292
18.1.1 Bopp pseudo-differential operators ............. 293
18.1.2 Bopp operators viewed as Weyl operators ........ 295
18.1.3 Adjoints and a composition formula ............. 297
18.1.4 Symplectic covariance of Bopp operators ........ 298
18.2 Intertwiners .......................................... 299
18.2.1 Windowed wavepacket transforms ................. 299
18.2.2 The intertwining property ...................... 302
18.3 Regularity results for Bopp operators ................. 303
18.3.1 Boundedness results ............................ 303
18.3.2 Global hypoellipticity properties .............. 304
19 Applications of Bopp Quantization
19.1 Spectral results for Bopp operators ................... 307
19.1.1 A fundamental property of the intertwiners ..... 307
19.1.2 Generalized eigenvalues and eigenvectors
of a Bopp operator ............................. 309
19.1.3 Application: the Landau problem ................ 312
19.2 Bopp calculus and deformation quantization ............ 314
19.2.1 Deformation quantization: motivation ........... 315
19.2.2 The Moyal product and bracket .................. 316
19.3 Non-commutative quantum mechanics ..................... 318
19.3.1 Background ..................................... 318
19.3.2 The operators 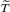 ω(z0) and Fω .................... 320
Bibliography .................................................. 325
Index ......................................................... 335 ω(z0) and Fω .................... 320
Bibliography .................................................. 325
Index ......................................................... 335
|