 | LeSage J.P. Introduction to spatial econometrics / J.LeSage, R.K.Pace. - Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009. - xiii, 354 p., [2] p. of plates: ill. (some col.), maps (some col.). - (Statistics, textbooks and monographs; 196.). - Ref.: p.323-336. - Ind.: p.337-354. - ISBN-13 978-1-4200-6424-7
|
1 Introduction ................................................. 1
1.1 Spatial dependence ...................................... 1
1.2 The spatial autoregressive process ...................... 8
1.2.1 Spatial autoregressive data generating
process ......................................... 12
1.3 An illustration of spatial spillovers .................. 16
1.4 The role of spatial econometric models ................. 20
1.5 The plan of the text ................................... 22
2 Motivating and Interpreting Spatial Econometric Models ...... 25
2.1 A time-dependence motivation ........................... 25
2.2 An omitted variables motivation ........................ 27
2.3 A spatial heterogeneity motivation ..................... 29
2.4 An externalities-based motivation ...................... 30
2.5 A model uncertainty motivation ......................... 30
2.6 Spatial autoregressive regression models ............... 32
2.7 Interpreting parameter estimates ....................... 33
2.7.1 Direct and indirect impacts in theory ........... 34
2.7.2 Calculating summary measures of impacts ......... 39
2.7.3 Measures of dispersion for the impact
estimates ....................................... 39
2.7.4 Partitioning the impacts by order of
neighbors ....................................... 40
2.7.5 Simplified alternatives to the impact
calculations .................................... 41
2.8 Chapter summary ........................................ 42
3 Maximum Likelihood Estimation ............................... 45
3.1 Model estimation ....................................... 46
3.1.1 SAR and SDM model estimation .................... 46
3.1.2 SEM model estimation ............................ 50
3.1.3 Estimates for models with two weight matrices ... 52
3.2 Estimates of dispersion for the parameters ............. 54
3.2.1 A mixed analytical-numerical Hessian
calculation ..................................... 56
3.2.2 A comparison of Hessian calculations ............ 59
3.3 Omitted variables with spatial dependence .............. 60
3.3.1 A Hausman test for OLS and SEM estimates ........ 61
3.3.2 Omitted variables bias of least-squares ......... 63
3.3.3 Omitted variables bias for spatial
regressions ..................................... 67
3.4 An applied example ..................................... 68
3.4.1 Coefficient estimates .......................... 69
3.4.2 Cumulative effects estimates .................... 70
3.4.3 Spatial partitioning of the impact estimates .... 72
3.4.4 A comparison of impacts from different models ... 73
3.5 Chapter summary ........................................ 75
4 Log-determinants and Spatial Weights ........................ 77
4.1 Determinants and transformations ....................... 77
4.2 Basic determinant computation .......................... 81
4.3 Determinants of spatial systems ........................ 84
4.3.1 Scalings and similarity transformations ......... 87
4.3.2 Determinant domain .............................. 88
4.3.3 Special cases ................................... 89
4.4 Monte Carlo approximation of the log-determinant ....... 96
4.4.1 Sensitivity of ρ estimates to approximation .... 100
4.5 Chebyshev approximation ............................... 105
4.6 Extrapolation ......................................... 108
4.7 Determinant bounds .................................... 108
4.8 Inverses and other functions .......................... 110
4.9 Expressions for interpretation of spatial models ...... 114
4.10 Closed-form solutions for single parameter spatial
models ................................................ 116
4.11 Forming spatial weights ............................... 118
4.12 Chapter summary ....................................... 120
5 Bayesian Spatial Econometric Models ........................ 123
5.1 Bayesian methodology .................................. 124
5.2 Conventional Bayesian treatment of the SAR model ...... 127
5.2.1 Analytical approaches to the Bayesian method ... 127
5.2.2 Analytical solution of the Bayesian spatial
model .......................................... 130
5.3 MCMC estimation of Bayesian spatial models ............ 133
5.3.1 Sampling conditional distributions ............. 133
5.3.2 Sampling for the parameter ρ ................... 136
5.4 The MCMC algorithm .................................... 139
5.5 An applied illustration ............................... 142
5.6 Uses for Bayesian spatial models ...................... 145
5.6.1 Robust heteroscedastic spatial regression ...... 146
5.6.2 Spatial effects estimates ...................... 149
5.6.3 Models with multiple weight matrices ........... 150
5.7 Chapter summary ....................................... 152
6 Model Comparison ........................................... 155
6.1 Comparison of spatial and non-spatial models .......... 155
6.2 An applied example of model comparison ................ 159
6.2.1 The data sample used ........................... 161
6.2.2 Comparing models with different weight
matrices ....................................... 161
6.2.3 A test for dependence in technical knowledge ... 163
6.2.4 A test of the common factor restriction ........ 164
6.2.5 Spatial effects estimates ...................... 165
6.3 Bayesian model comparison ............................. 168
6.3.1 Comparing models based on different weights .... 169
6.3.2 Comparing models based on different
variables ...................................... 173
6.3.3 An applied illustration of model comparison .... 175
6.3.4 An illustration of MC3 and model averaging ..... 178
6.4 Chapter summary ....................................... 184
6.5 Chapter appendix ...................................... 185
7 Spatiotemporal and Spatial Models .......................... 189
7.1 Spatiotemporal partial adjustment model ............... 190
7.2 Relation between spatiotemporal and SAR models ........ 191
7.3 Relation between spatiotemporal and SEM models ........ 196
7.4 Covariance matrices ................................... 197
7.4.1 Monte Carlo experiment ......................... 200
7.5 Spatial econometric and statistical models ............ 201
7.6 Patterns of temporal and spatial dependence ........... 203
7.7 Chapter summary ....................................... 207
8 Spatial Econometric Interaction Models ..................... 211
8.1 Interregional flows in a spatial regression context ... 212
8.2 Maximum likelihood and Bayesian estimation ............ 218
8.3 Application of the spatial econometric interaction
model ................................................. 223
8.4 Extending the spatial econometric interaction model ... 228
8.4.1 Adjusting spatial weights using prior
knowledge ...................................... 229
8.4.2 Adjustments to address the zero flow problem ... 230
8.4.3 Spatially structured multilateral resistance
effects ........................................ 232
8.4.4 Flows as a rare event .......................... 234
8.5 Chapter summary ....................................... 236
9 Matrix Exponential Spatial Models .......................... 237
9.1 The MESS model ........................................ 237
9.1.1 The matrix exponential ......................... 238
9.1.2 Maximum likelihood estimation .................. 239
9.1.3 A closed form solution for the parameters ...... 240
9.1.4 An applied illustration ........................ 241
9.2 Spatial error models using MESS ....................... 243
9.2.1 Spatial model Monte Carlo experiments .......... 246
9.2.2 An applied illustration ........................ 247
9.3 A Bayesian version of the model ....................... 250
9.3.1 The posterior for α ............................ 250
9.3.2 The posterior for β ............................ 252
9.3.3 Applied illustrations .......................... 253
9.4 Extensions of the model ............................... 255
9.4.1 More flexible weights .......................... 255
9.4.2 MCMC estimation ................................ 256
9.4.3 MCMC estimation of the model ................... 257
9.4.4 The conditional distributions for β, σ and
V .............................................. 258
9.4.5 Computational considerations ................... 259
9.4.6 An illustration of the extended model .......... 260
9.5 Fractional differencing ............................... 265
9.5.1 Empirical illustrations ........................ 270
9.5.2 Computational considerations ................... 275
9.6 Chapter summary ....................................... 277
10 Limited Dependent Variable Spatial Models .................. 279
10.1 Bayesian latent variable treatment .................... 281
10.1.1 The SAR probit model ........................... 283
10.1.2 An MCMC sampler for the SAR probit model ....... 284
10.1.3 Gibbs sampling the conditional distribution
for y* ......................................... 285
10.1.4 Some observations regarding implementation ..... 287
10.1.5 Applied illustrations of the spatial probit
model .......................................... 289
10.1.6 Marginal effects for the spatial probit
model .......................................... 293
10.2 The ordered spatial probit model ...................... 297
10.3 Spatial Tobit models .................................. 299
10.3.1 An example of the spatial Tobit model .......... 302
10.4 The multinomial spatial probit model .................. 306
10.4.1 The MCMC sampler for the SAR MNP model ......... 307
10.4.2 Sampling for β and ρ ........................... 308
10.4.3 Sampling for Σ ................................. 308
10.4.4 Sampling for 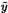 * ................................ 310
10.5 An applied illustration of spatial MNP ................ 312
10.5.1 Effects estimates for the spatial MNP model .... 314
10.6 Spatially structured effects probit models ............ 316
10.7 Chapter summary ....................................... 320
References .................................................... 323
Index ......................................................... 337 * ................................ 310
10.5 An applied illustration of spatial MNP ................ 312
10.5.1 Effects estimates for the spatial MNP model .... 314
10.6 Spatially structured effects probit models ............ 316
10.7 Chapter summary ....................................... 320
References .................................................... 323
Index ......................................................... 337
|
|