Preface ........................................................ xi
Tables of widely used symbols .................................. xv
1 Introduction ................................................. 1
1.1 The intrinsic liquid/vapor interface .................... 3
1.2 Surface-induced order ................................... 7
1.2.1 Surface layering ................................. 7
1.2.2 In-plane surface order ........................... 7
1.3 Capillary waves on the liquid surface ................... 9
1.4 Thin liquid films ...................................... 15
1.5 Buried interfaces ...................................... 16
1.6 Optical methods ........................................ 17
1.6.1 Ellipsometry .................................... 17
1.6.2 Non-linear optics ............................... 18
1.7 X-ray surface methods .................................. 20
1.8 Further reading ........................................ 22
1.8.1 X-ray physics ................................... 22
1.8.2 Capillary wave theory ........................... 22
1.8.3 Soft matter ..................................... 22
1.9 References ............................................. 22
2 Instrumentation ............................................. 29
2.1 Introduction ........................................... 29
2.2 Liquid-surface reflectometers .......................... 30
2.3 Kinematics of scattering from liquid surfaces and
interfaces ............................................. 32
2.4 Overview of the first type of liquid-surface
scattering instrument .................................. 34
2.4.1 Steering crystal: simple tracking ............... 38
2.5 Detailed full alignment ................................ 40
2.5.1 Optical prealignment ............................ 40
2.5.2 X-ray alignment: first steps .................... 41
2.5.3 Steering-crystal alignment ...................... 42
Centering the steering-crystal face on the
synchrotron beam ................................ 42
Equations for the miscut and the effect of
η ≠ 0 ........................................... 43
Correcting for the miscut ....................... 45
Correcting for η ≠ 0 ............................ 46
2.5.4 Input-arm tracking: equations ................... 46
Equations for the incident wave vector when
using a bt stage ................................ 47
2.5.5 Input-arm, sample-stage, and output-arm
alignment ....................................... 48
Preliminary input-arm zero ...................... 48
Input-arm tracking and setting L1 ............... 49
First sample reflection and setting L2 and L3 ... 50
Precise X-ray determination of αi = 0 for a
flat sample ..................................... 53
Alignment with curved samples ................... 54
Aligning the guard slit S2 and setting the
zero of the output-arm rotation ................. 60
2.5.6 The output (detector) arm for grazing-
incidence diffraction ........................... 60
Two-slit arm .................................... 60
Angular-selection arm ........................... 62
Area detector ................................... 63
2.5.7 Reflectometer motions as a function of 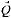 ........ 64
Qz dependence for reflectometer with
base-tilt (bt) stage ............................ 64
2.6 Overview of the second type of liquid-surface
scattering instrument .................................. 65
2.6.1 Practical issues for the second type of
reflectometer ................................... 68
2.6.2 First vs. second type of instrument ............. 70
2.7 Detectors .............................................. 71
2.7.1 Gas-ionization detectors ........................ 71
2.7.2 Scintillation detectors ......................... 72
2.7.3 Photodiodes ..................................... 73
2.7.4 Position-sensitive linear detector (PSD-1D) ..... 74
2.7.5 Position-sensitive area detector (PSD-2D) ....... 74
2.8 Absorber calibration ................................... 77
2.9 Non-synchrotron-based liquid-surface reflectometers .... 78
2.9.1 Fixed X-ray sources ............................. 78
2.9.2 Butterfly-type reflectometers ................... 80
2.10 Addenda ................................................ 81
2.10.1 Bragg reflection ................................ 81
2.10.2 Alignment without a tilt stage .................. 84
Equations for the incident wave vector in the
absence of the bt stage ......................... 84
The Qz dependence for a reflectometer without
a bt stage ...................................... 85
2.11 References ............................................. 85
3 Theory of X-ray scattering from liquid surfaces ............. 88
3.1 Introduction ........................................... 89
3.2 Overview of the theory ................................. 92
3.3 Reflection from an idealized flat surface: the
Fresnel reflectivity ................................... 94
3.4 Reflection from less idealized surfaces ................ 99
3.4.1 The Parratt method .............................. 99
3.4.2 The master-formula approximation ............... 104
3.5 The Born approximation ................................ 107
3.5.1 General development ............................ 107
3.6 Examples of applications for flat surfaces ............ 112
3.6.1 The surface structure factor Φeff(Qz) .......... 112
3.6.2 The surface structure factor for layered
surfaces ....................................... 116
3.6.3 The Patterson function ......................... 118
3.7 The effect of thermal roughness ....................... 121
3.7.1 Resolution effects on the capillary-roughness
model .......................................... 125
Diffuse scattering: numerical integration ...... 125
Specular reflectivity: numerical integration ... 130
Specular reflectivity: analytic approximation .. 131
Specular reflectivity: circular resolution
function ....................................... 134
Diffuse scattering: analytic approximation ..... 135
3.8 The distorted-wave approximation (DWA) ................ 136
3.8.1 Formal development ............................. 138
3.8.2 Sample applications of the DWA ................. 142
Scattering from a thin surface layer ........... 142
Height fluctuations ............................ 144
Grazing-incidence diffraction (GID) from
two-dimensional surface order .................. 145
3.9 Scattering from a thick film .......................... 146
3.9.1 The DWA cross section .......................... 147
3.9.2 Internal thermal fluctuations .................. 150
3.9.3 The Born approximation ......................... 151
3.10 Effects of X-ray coherence and macroscopic surface
inhomogeneities on specular reflectivity .............. 160
3.11 X-ray photon-correlation spectroscopy ................. 163
3.12 Addenda ............................................... 165
3.12.1 Realistic integration of capillary
fluctuations ................................... 165
3.12.2 Effective van der Waals interaction ............ 167
3.13 References ............................................ 169
4 Experiments on liquid surfaces and interfaces .............. 173
4.1 Liquid/vapor interfaces without observable structure .. 178
4.1.1 The surface of water ........................... 178
4.1.2 Other non-structured liquid surfaces ........... 184
4.2 Surfaces exhibiting structure ......................... 186
4.2.1 Liquid crystals ................................ 188
4.2.2 Liquid metals .................................. 197
Elemental metals ............................... 197
Alloys: Gibbs adsorption ....................... 205
Alloys: surface freezing ....................... 206
4.2.3 Two-dimensional molecular surface freezing ..... 214
Surface freezing of alkanes and alcohols ....... 214
4.2.4 Langmuir monolayers ............................ 220
Langmuir monolayers of amphiphilic molecules
with long alkyl chains ......................... 223
Charged Langmuir monolayers and interactions
with subphase ions ............................. 228
Langmuir monolayers relevant to biological
processes and biomaterials ..................... 232
Langmuir monolayers of nanoparticles ........... 236
Langmuir monolayers of polymers ................ 240
4.3 Interfaces between thin macroscopic liquid films and
a bulk liquid ......................................... 244
4.3.1 Ga-Bi .......................................... 246
4.3.2 Vapor-controlled thin liquid wetting films ..... 250
Controlled wetting ............................. 250
Thin macroscopic single-component liquid
wetting layers on bulk substrate ............... 250
Thin macroscopic binary wetting layers on
bulk substrate ................................. 261
4.4 Deeply buried liquid/liquid interfaces ................ 265
4.4.1 Neat liquid/liquid interfaces and special
techniques for their study ..................... 265
4.4.2 Liquid/liquid interfaces with surfactants ...... 270
Head-group packing: oil/water vs. air/water .... 271
Phase transitions .............................. 272
Reflectivity from inhomogeneous interfaces ..... 275
Ultra-low-tension interfaces ................... 278
4.4.3 Ion distributions .............................. 278
4.5 Time-dependent surface fluctuations ................... 281
4.6 References ............................................ 285
Index ......................................................... 300 ........ 64
Qz dependence for reflectometer with
base-tilt (bt) stage ............................ 64
2.6 Overview of the second type of liquid-surface
scattering instrument .................................. 65
2.6.1 Practical issues for the second type of
reflectometer ................................... 68
2.6.2 First vs. second type of instrument ............. 70
2.7 Detectors .............................................. 71
2.7.1 Gas-ionization detectors ........................ 71
2.7.2 Scintillation detectors ......................... 72
2.7.3 Photodiodes ..................................... 73
2.7.4 Position-sensitive linear detector (PSD-1D) ..... 74
2.7.5 Position-sensitive area detector (PSD-2D) ....... 74
2.8 Absorber calibration ................................... 77
2.9 Non-synchrotron-based liquid-surface reflectometers .... 78
2.9.1 Fixed X-ray sources ............................. 78
2.9.2 Butterfly-type reflectometers ................... 80
2.10 Addenda ................................................ 81
2.10.1 Bragg reflection ................................ 81
2.10.2 Alignment without a tilt stage .................. 84
Equations for the incident wave vector in the
absence of the bt stage ......................... 84
The Qz dependence for a reflectometer without
a bt stage ...................................... 85
2.11 References ............................................. 85
3 Theory of X-ray scattering from liquid surfaces ............. 88
3.1 Introduction ........................................... 89
3.2 Overview of the theory ................................. 92
3.3 Reflection from an idealized flat surface: the
Fresnel reflectivity ................................... 94
3.4 Reflection from less idealized surfaces ................ 99
3.4.1 The Parratt method .............................. 99
3.4.2 The master-formula approximation ............... 104
3.5 The Born approximation ................................ 107
3.5.1 General development ............................ 107
3.6 Examples of applications for flat surfaces ............ 112
3.6.1 The surface structure factor Φeff(Qz) .......... 112
3.6.2 The surface structure factor for layered
surfaces ....................................... 116
3.6.3 The Patterson function ......................... 118
3.7 The effect of thermal roughness ....................... 121
3.7.1 Resolution effects on the capillary-roughness
model .......................................... 125
Diffuse scattering: numerical integration ...... 125
Specular reflectivity: numerical integration ... 130
Specular reflectivity: analytic approximation .. 131
Specular reflectivity: circular resolution
function ....................................... 134
Diffuse scattering: analytic approximation ..... 135
3.8 The distorted-wave approximation (DWA) ................ 136
3.8.1 Formal development ............................. 138
3.8.2 Sample applications of the DWA ................. 142
Scattering from a thin surface layer ........... 142
Height fluctuations ............................ 144
Grazing-incidence diffraction (GID) from
two-dimensional surface order .................. 145
3.9 Scattering from a thick film .......................... 146
3.9.1 The DWA cross section .......................... 147
3.9.2 Internal thermal fluctuations .................. 150
3.9.3 The Born approximation ......................... 151
3.10 Effects of X-ray coherence and macroscopic surface
inhomogeneities on specular reflectivity .............. 160
3.11 X-ray photon-correlation spectroscopy ................. 163
3.12 Addenda ............................................... 165
3.12.1 Realistic integration of capillary
fluctuations ................................... 165
3.12.2 Effective van der Waals interaction ............ 167
3.13 References ............................................ 169
4 Experiments on liquid surfaces and interfaces .............. 173
4.1 Liquid/vapor interfaces without observable structure .. 178
4.1.1 The surface of water ........................... 178
4.1.2 Other non-structured liquid surfaces ........... 184
4.2 Surfaces exhibiting structure ......................... 186
4.2.1 Liquid crystals ................................ 188
4.2.2 Liquid metals .................................. 197
Elemental metals ............................... 197
Alloys: Gibbs adsorption ....................... 205
Alloys: surface freezing ....................... 206
4.2.3 Two-dimensional molecular surface freezing ..... 214
Surface freezing of alkanes and alcohols ....... 214
4.2.4 Langmuir monolayers ............................ 220
Langmuir monolayers of amphiphilic molecules
with long alkyl chains ......................... 223
Charged Langmuir monolayers and interactions
with subphase ions ............................. 228
Langmuir monolayers relevant to biological
processes and biomaterials ..................... 232
Langmuir monolayers of nanoparticles ........... 236
Langmuir monolayers of polymers ................ 240
4.3 Interfaces between thin macroscopic liquid films and
a bulk liquid ......................................... 244
4.3.1 Ga-Bi .......................................... 246
4.3.2 Vapor-controlled thin liquid wetting films ..... 250
Controlled wetting ............................. 250
Thin macroscopic single-component liquid
wetting layers on bulk substrate ............... 250
Thin macroscopic binary wetting layers on
bulk substrate ................................. 261
4.4 Deeply buried liquid/liquid interfaces ................ 265
4.4.1 Neat liquid/liquid interfaces and special
techniques for their study ..................... 265
4.4.2 Liquid/liquid interfaces with surfactants ...... 270
Head-group packing: oil/water vs. air/water .... 271
Phase transitions .............................. 272
Reflectivity from inhomogeneous interfaces ..... 275
Ultra-low-tension interfaces ................... 278
4.4.3 Ion distributions .............................. 278
4.5 Time-dependent surface fluctuations ................... 281
4.6 References ............................................ 285
Index ......................................................... 300
|