Preface ...................................................... xiii
About the Editors .............................................. xv
Contributing Authors ......................................... xvii
Notations and Symbols ......................................... xix
Abbreviations ................................................. xxv
CHAPTER 1 Fundamentals of Time-Varying Communication Channels .. 1
1.1 Introduction ............................................... 1
1.2 The Physics of Time-Varying Channels ....................... 2
1.2.1 Wave Propagation .................................... 2
1.2.2 Multipath Propagation and Time Dispersion ........... 2
1.2.3 Doppler Effect and Frequency Dispersion ............. 4
1.2.4 Path Loss and Fading ................................ 6
1.2.5 Spatial Characteristics ............................. 6
1.3 Deterministic Description .................................. 7
1.3.1 Delay-Doppler Domain - Spreading Function ........... 7
1.3.2 Delay-Scale Domain - Delay-Scale Spreading
Function ............................................ 9
1.3.3 Time-Frequency Domain - Time-Varying Transfer
Function ........................................... 10
1.3.4 Time-Delay Domain - Time-Varying Impulse Response .. 11
1.3.5 Extension to Multiantenna Systems .................. 12
1.4 Stochastic Description .................................... 14
1.4.1 WSSUS Channels ..................................... 15
1.4.2 Extension to Multiantenna Systems .................. 20
1.4.3 Non-WSSUS Channels ................................. 23
1.5 Underspread Channels ...................................... 29
1.5.1 Dispersion-Underspread Property .................... 30
1.5.2 Correlation-Underspread Property ................... 32
1.5.3 Approximate Eigenrelation .......................... 33
1.5.4 Time-Frequency Sampling ............................ 37
1.5.5 Approximate Karhunen-Loeve Expansion ............... 38
1.6 Parsimonious Channel Models ............................... 40
1.6.1 Basis Expansion Models ............................. 41
1.6.2 Parsimonious WSSUS Models .......................... 44
1.6.3 Parsimonious Non-WSSUS Models ...................... 46
1.7 Measurement ............................................... 48
1.7.1 Spread-Spectrum-Like Channel Sounding .............. 48
1.7.2 Multicarrier Channel Sounding ...................... 52
1.7.3 Extension to Multiantenna Systems .................. 54
1.7.4 Measurement of Second-Order Statistics ............. 55
1.8 Conclusion ................................................ 59
Acknowledgment ............................................ 59
References ................................................ 59
CHAPTER 2 Information Theory of Underspread WSSUS Channels .... 65
2.1 The Role of a System Model ................................ 65
2.1.1 A Realistic Model .................................. 65
2.1.2 A Brief Literature Survey .......................... 66
2.1.3 Capacity Bounds Answering Engineering-Relevant
Questions .......................................... 68
2.2 A Discretized System Model ................................ 69
2.2.1 The Channel Model .................................. 69
2.2.2 Discretization of the Continuous-Time Input-
Output Relation .................................... 71
2.3 The Large-Bandwidth Regime: Diagonalized I/O Relation ..... 82
2.3.1 Power Constraints .................................. 83
2.3.2 Definition of Noncoherent Capacity ................. 84
2.3.3 A Coherent-Capacity Upper Bound .................... 84
2.3.4 An Upper Bound on Capacity that Is Explicit in
СH (τ, ν) .......................................... 84
2.3.5 A Lower Bound on Capacity .......................... 88
2.3.6 A Numerical Example ................................ 90
2.3.7 Extension to the Multiantenna Setting .............. 92
2.3.8 Numerical Examples ................................. 94
2.4 The Large-Bandwidth Regime: I/O Relation with
Interference .............................................. 97
2.4.1 A Lower Bound on Capacity .......................... 97
2.4.2 Numerical Examples ................................ 104
2.5 The High-SNR Regime ...................................... 106
2.5.1 A Lower Bound on Capacity ......................... 106
2.5.2 Numerical Examples ................................ 108
2.6 Conclusions .............................................. 110
References ............................................... 112
CHAPTER 3 Algebraic Coding for Fast Fading Channels .......... 117
3.1 Introduction ............................................. 117
3.1.1 Fading Channel Model .............................. 118
3.1.2 System Model ...................................... 118
3.2 Product Distance Based Code Design ....................... 119
3.2.1 Signal Space Diversity and Product Distance ....... 119
3.2.2 Lattice Constellations ............................ 122
3.3 Lattices ................................................. 122
3.3.1 First Definitions ................................. 122
3.3.2 Sublattices and Equivalent Lattices ............... 125
3.4 Algebraic Number Theory .................................. 127
3.4.1 Algebraic Number Fields ........................... 127
3.4.2 Integral Basis and Canonical Embeddings ........... 130
3.5 Algebraic Lattices ....................................... 132
3.6 Ideal Lattices ........................................... 135
3.7 Algebraic Rotations with High Product Distance ........... 137
3.7.1 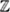 n Ideal Lattices ................................. 137
3.7.2 Rotated n Ideal Lattices ................................. 137
3.7.2 Rotated 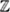 n-Lattice Codes .......................... 138
3.7.3 A Simple Two-Dimensional Rotation Based on the
Golden Number ..................................... 139
3.7.4 The Cyclotomic Construction ....................... 140
3.8 Sphere Decoding .......................................... 144
3.8.1 The Sphere Decoder Algorithm ...................... 145
3.8.2 The Sphere Decoder with Fading .................... 150
3.9 Performance of Rotated Constellations .................... 150
3.10 Conclusions .............................................. 151
References ............................................... 152
CHAPTER 4 Estimation of Time-Varying Channels - A Block
Approach ...................................................... 155
4.1 Introduction ............................................. 155
4.2 System and Channel Model ................................. 156
4.2.1 System Model ...................................... 156
4.2.2 BEM Channel Model ................................. 158
4.3 Channel Estimation Based on a Single Block ............... 160
4.3.1 Introduction ...................................... 160
4.3.2 Channel Estimation Data Model ..................... 161
4.3.3 Channel Estimators ................................ 166
4.3.4 Channel Identifiability ........................... 170
4.3.5 Simulation Results ................................ 174
4.4 Channel Estimation Based on Multiple Blocks .............. 180
4.4.1 Introduction ...................................... 180
4.4.2 Data Model and BEM for Multiple OFDM Symbols ...... 183
4.4.3 Channel Identifiability Based on Multiple Blocks .. 184
4.4.4 Simulation Results ................................ 186
4.5 Extension to MIMO Systems ................................ 189
4.5.1 Introduction ...................................... 189
4.5.2 Single-Carrier System ............................. 189
4.5.3 OFDM System ....................................... 190
4.6 Adaptive Channel Estimation .............................. 192
4.7 Conclusions .............................................. 194
References ............................................... 194
CHAPTER 5 Pilot Design and Optimization for Transmission
over Time-Varying Channels .................................... 199
5.1 Introduction ............................................. 199
5.2 Pilot Design: A Framework ................................ 200
5.2.1 Modeling of Pilot-Assisted Transmission ........... 200
5.2.2 Transceiver Architectures ......................... 202
5.2.3 Performance Criteria .............................. 203
5.3 Optimal TDM Pilot Insertion Pattern in Single Carrier
Systems .................................................. 204
5.3.1 Channel Model ..................................... 205
5.3.2 Periodic TDM Pilot Placement ...................... 205
5.3.3 Receiver Structure ................................ 206
5.3.4 Optimization Criteria ............................. 208
5.3.5 Optimal TDM Pilot Placement ....................... 209
5.3.6 Bibliographical Notes ............................. 213
5.4 Alternative Pilot Insertion Strategy - Superimposed
Training ................................................. 214
5.4.1 Kalman Tracking with Superimposed Training ........ 214
5.4.2 Superimposed versus TDM Schemes: Performance
Comparison ........................................ 216
5.4.3 Bibliographical Notes ............................. 218
5.5 Resource Allocation: Amount of Training and Power
Optimization ............................................. 220
5.5.1 Cutoff Rate Analysis .............................. 220
5.5.2 Bibliographical Notes ............................. 224
5.6 Pilot Design for МГМО Channels ........................... 224
5.7 Pilot Design for Wideband Systems ........................ 225
5.7.1 OFDMA Systems ..................................... 225
5.7.2 CDMA Systems ...................................... 227
5.7.3 Ultra Wideband .................................... 227
5.8 Conclusion ............................................... 227
Acknowledgment ........................................... 228
5.A The Kalman Filter for TDM Training .................. 228
5.В Proof of Proposition 5.1 ............................ 228
5.C Proof of Lemma 5.1 .................................. 230
5.D Proof of Theorem 5.1 ................................ 231
References ............................................... 233
CHAPTER 6 Equalization of Time-Varying Channels .............. 237
6.1 Introduction ............................................. 237
6.2 System Model ............................................. 239
6.2.1 Basic Assumptions ................................. 239
6.2.2 The Structure of the Effective Channel Matrix Q ... 240
6.3 Coherent Equalization .................................... 245
6.3.1 Coherent Equalization Criteria .................... 245
6.3.2 Coherent Equalization Tools ....................... 247
6.3.3 Coherent Equalization for Time-Frequency
Concentrated Modulation/Demodulation .............. 256
6.3.4 Coherent Equalization of Single-Carrier
Modulation/Demodulation ........................... 259
6.4 Noncoherent Equalization ................................. 260
6.4.1 Noncoherent System Model .......................... 261
6.4.2 Noncoherent Equalization Criteria ................. 262
6.4.3 Noncoherent Equalization Tools .................... 265
6.4.4 Noncoherent Equalization for Single-Carrier
Modulation/Demodulation ........................... 270
6.4.5 Noncoherent Equalization for Time-Frequency
Concentrated Modulation/Demodulation .............. 272
6.5 Conclusion ............................................... 273
6.A Derivation of Posterior LLR Expression (6.36) ............ 274
6.B Derivation of the Noncoherent MLSD Expression (6.73) ..... 274
6.C Explanation of EM Recursion (6.91) ....................... 275
6.D Info EM(B) Algorithms for Noncoherent Equalization ....... 276
References ............................................... 277
CHAPTER 7 OFDM Communications over Time-Varying Channels ..... 285
7.1 OFDM Systems ............................................. 285
7.1.1 System Model ...................................... 286
7.1.2 Effects of Rapidly Time-Varying Channels .......... 291
7.1.3 МГМО-OFDM ......................................... 297
7.2 ICI Mitigation Techniques ................................ 299
7.2.1 Linear Equalization ............................... 299
7.2.2 Nonlinear Equalization ............................ 306
7.2.3 Transmitter Preprocessing ......................... 313
7.2.4 Extension to MIMO-OFDM ............................ 317
7.3 Time-Varying Channel Estimation .......................... 318
7.3.1 Basis Expansion Model of LTV Channels ............. 319
7.3.2 Training-Based Channel Estimation ................. 320
7.3.3 Iterative Channel Estimation and Turbo
Equalization ...................................... 324
7.3.4 Impact of Channel Estimation on BER Performance ... 325
7.3.5 Channel Estimation in MIMO-OFDM ................... 325
7.4 Concluding Remarks ....................................... 327
7.4.1 System and Application Aspects .................... 327
7.4.2 Open Issues ....................................... 328
References ............................................... 329
CHAPTER 8 Multiuser MIMO Receiver Processing for Time-
Varying Channels .............................................. 337
8.1 Introduction ............................................. 337
8.2 Multiuser MIMO Systems ................................... 338
8.3 Tools for Complexity Reduction ........................... 341
8.3.1 Iterative Approximation of the MAP Detector ....... 341
8.3.2 Reduced-Rank Model for the Time-Varying Channel ... 343
8.3.3 The Krylov Subspace Method ........................ 345
8.3.4 Sphere Decoding ................................... 348
8.4 Iterative Multiuser MIMO Time-Varying Channel
Estimation ............................................... 352
8.4.1 Signal Model ...................................... 352
8.4.2 Reduced-Rank LMMSE Channel Estimator .............. 353
8.4.3 Comparison of the Slepian and Fourier Bases ....... 354
8.4.4 Krylov Approximation of the Reduced-Rank LMMSE
Channel Estimator ................................. 355
8.5 Linear Joint Antenna Multiuser Detection ................. 355
8.5.1 Multiuser Detection in Chip Space ................. 355
8.5.2 Multiuser Detection in User Space ................. 356
8.6 Nonlinear Detection ...................................... 358
8.6.1 Exploiting the Reduced-Rank Channel Model ......... 358
8.6.2 Soft Sphere Decoding .............................. 361
8.6.3 Computational Complexity .......................... 362
8.7 Simulation Results ....................................... 364
8.7.1 Bit Error Rate Comparison ......................... 364
8.7.2 Computational Complexity Comparison ............... 366
8.8 Conclusions .............................................. 368
Acknowledgments .......................................... 369
8.A Computation of the Log-Likelihood Ratio (8.44) ........... 369
References ............................................... 371
CHAPTER 9 Time-Scale and Dispersive Processing for Wideband
Time-Varying Channels ......................................... 375
9.1 Introduction ............................................. 375
9.1.1 Need for Wideband Channel Characterizations ....... 375
9.1.2 Examples of Wideband Dispersive Channel
Characteristics ................................... 377
9.1.3 Chapter Organization .............................. 380
9.2 Narrowband Channel Characterization ...................... 381
9.2.1 Narrowband Spreading Function ..................... 381
9.2.2 Discrete Channel Characterization and Finite
Approximations .................................... 381
9.3 Wideband Delay-Scale Channel Characterization ............ 383
9.3.1 Narrowband and Wideband Conditions ................ 383
9.3.2 Wideband Spreading Function ....................... 384
9.3.3 Discrete Delay-Scale Channel Characterization ..... 384
9.3.4 Finite Approximations ............................. 386
9.3.5 Multipath-Scale Diversity ......................... 387
9.3.6 Time-Scale Rake Receiver .......................... 389
9.4 Wideband Dispersive Channel Characterization ............. 392
9.4.1 Dispersive Time-Frequency Structures .............. 392
9.4.2 Dispersive Spreading Function and Unitary
Warping Relations ................................. 393
9.4.3 Discrete Dispersive Channel with Physical
Limitations ....................................... 394
9.4.4 Generalized Time-Frequency Rake Receiver .......... 395
9.5 Underwater Wireless Communication Channels ............... 396
9.5.1 Shallow Water Environment Model ................... 396
9.5.2 Time-Frequency Characteristics of Shallow Water
Environments ...................................... 398
9.5.3 Mode Separation in Time-Frequency ................. 398
9.5.4 Dispersion Diversity Receiver Design .............. 400
9.5.5 Numerical Simulations for Shallow Water
Communications .................................... 403
9.6 Application Example ...................................... 405
9.7 Conclusions .............................................. 410
References ............................................... 411
Index ......................................................... 417 n-Lattice Codes .......................... 138
3.7.3 A Simple Two-Dimensional Rotation Based on the
Golden Number ..................................... 139
3.7.4 The Cyclotomic Construction ....................... 140
3.8 Sphere Decoding .......................................... 144
3.8.1 The Sphere Decoder Algorithm ...................... 145
3.8.2 The Sphere Decoder with Fading .................... 150
3.9 Performance of Rotated Constellations .................... 150
3.10 Conclusions .............................................. 151
References ............................................... 152
CHAPTER 4 Estimation of Time-Varying Channels - A Block
Approach ...................................................... 155
4.1 Introduction ............................................. 155
4.2 System and Channel Model ................................. 156
4.2.1 System Model ...................................... 156
4.2.2 BEM Channel Model ................................. 158
4.3 Channel Estimation Based on a Single Block ............... 160
4.3.1 Introduction ...................................... 160
4.3.2 Channel Estimation Data Model ..................... 161
4.3.3 Channel Estimators ................................ 166
4.3.4 Channel Identifiability ........................... 170
4.3.5 Simulation Results ................................ 174
4.4 Channel Estimation Based on Multiple Blocks .............. 180
4.4.1 Introduction ...................................... 180
4.4.2 Data Model and BEM for Multiple OFDM Symbols ...... 183
4.4.3 Channel Identifiability Based on Multiple Blocks .. 184
4.4.4 Simulation Results ................................ 186
4.5 Extension to MIMO Systems ................................ 189
4.5.1 Introduction ...................................... 189
4.5.2 Single-Carrier System ............................. 189
4.5.3 OFDM System ....................................... 190
4.6 Adaptive Channel Estimation .............................. 192
4.7 Conclusions .............................................. 194
References ............................................... 194
CHAPTER 5 Pilot Design and Optimization for Transmission
over Time-Varying Channels .................................... 199
5.1 Introduction ............................................. 199
5.2 Pilot Design: A Framework ................................ 200
5.2.1 Modeling of Pilot-Assisted Transmission ........... 200
5.2.2 Transceiver Architectures ......................... 202
5.2.3 Performance Criteria .............................. 203
5.3 Optimal TDM Pilot Insertion Pattern in Single Carrier
Systems .................................................. 204
5.3.1 Channel Model ..................................... 205
5.3.2 Periodic TDM Pilot Placement ...................... 205
5.3.3 Receiver Structure ................................ 206
5.3.4 Optimization Criteria ............................. 208
5.3.5 Optimal TDM Pilot Placement ....................... 209
5.3.6 Bibliographical Notes ............................. 213
5.4 Alternative Pilot Insertion Strategy - Superimposed
Training ................................................. 214
5.4.1 Kalman Tracking with Superimposed Training ........ 214
5.4.2 Superimposed versus TDM Schemes: Performance
Comparison ........................................ 216
5.4.3 Bibliographical Notes ............................. 218
5.5 Resource Allocation: Amount of Training and Power
Optimization ............................................. 220
5.5.1 Cutoff Rate Analysis .............................. 220
5.5.2 Bibliographical Notes ............................. 224
5.6 Pilot Design for МГМО Channels ........................... 224
5.7 Pilot Design for Wideband Systems ........................ 225
5.7.1 OFDMA Systems ..................................... 225
5.7.2 CDMA Systems ...................................... 227
5.7.3 Ultra Wideband .................................... 227
5.8 Conclusion ............................................... 227
Acknowledgment ........................................... 228
5.A The Kalman Filter for TDM Training .................. 228
5.В Proof of Proposition 5.1 ............................ 228
5.C Proof of Lemma 5.1 .................................. 230
5.D Proof of Theorem 5.1 ................................ 231
References ............................................... 233
CHAPTER 6 Equalization of Time-Varying Channels .............. 237
6.1 Introduction ............................................. 237
6.2 System Model ............................................. 239
6.2.1 Basic Assumptions ................................. 239
6.2.2 The Structure of the Effective Channel Matrix Q ... 240
6.3 Coherent Equalization .................................... 245
6.3.1 Coherent Equalization Criteria .................... 245
6.3.2 Coherent Equalization Tools ....................... 247
6.3.3 Coherent Equalization for Time-Frequency
Concentrated Modulation/Demodulation .............. 256
6.3.4 Coherent Equalization of Single-Carrier
Modulation/Demodulation ........................... 259
6.4 Noncoherent Equalization ................................. 260
6.4.1 Noncoherent System Model .......................... 261
6.4.2 Noncoherent Equalization Criteria ................. 262
6.4.3 Noncoherent Equalization Tools .................... 265
6.4.4 Noncoherent Equalization for Single-Carrier
Modulation/Demodulation ........................... 270
6.4.5 Noncoherent Equalization for Time-Frequency
Concentrated Modulation/Demodulation .............. 272
6.5 Conclusion ............................................... 273
6.A Derivation of Posterior LLR Expression (6.36) ............ 274
6.B Derivation of the Noncoherent MLSD Expression (6.73) ..... 274
6.C Explanation of EM Recursion (6.91) ....................... 275
6.D Info EM(B) Algorithms for Noncoherent Equalization ....... 276
References ............................................... 277
CHAPTER 7 OFDM Communications over Time-Varying Channels ..... 285
7.1 OFDM Systems ............................................. 285
7.1.1 System Model ...................................... 286
7.1.2 Effects of Rapidly Time-Varying Channels .......... 291
7.1.3 МГМО-OFDM ......................................... 297
7.2 ICI Mitigation Techniques ................................ 299
7.2.1 Linear Equalization ............................... 299
7.2.2 Nonlinear Equalization ............................ 306
7.2.3 Transmitter Preprocessing ......................... 313
7.2.4 Extension to MIMO-OFDM ............................ 317
7.3 Time-Varying Channel Estimation .......................... 318
7.3.1 Basis Expansion Model of LTV Channels ............. 319
7.3.2 Training-Based Channel Estimation ................. 320
7.3.3 Iterative Channel Estimation and Turbo
Equalization ...................................... 324
7.3.4 Impact of Channel Estimation on BER Performance ... 325
7.3.5 Channel Estimation in MIMO-OFDM ................... 325
7.4 Concluding Remarks ....................................... 327
7.4.1 System and Application Aspects .................... 327
7.4.2 Open Issues ....................................... 328
References ............................................... 329
CHAPTER 8 Multiuser MIMO Receiver Processing for Time-
Varying Channels .............................................. 337
8.1 Introduction ............................................. 337
8.2 Multiuser MIMO Systems ................................... 338
8.3 Tools for Complexity Reduction ........................... 341
8.3.1 Iterative Approximation of the MAP Detector ....... 341
8.3.2 Reduced-Rank Model for the Time-Varying Channel ... 343
8.3.3 The Krylov Subspace Method ........................ 345
8.3.4 Sphere Decoding ................................... 348
8.4 Iterative Multiuser MIMO Time-Varying Channel
Estimation ............................................... 352
8.4.1 Signal Model ...................................... 352
8.4.2 Reduced-Rank LMMSE Channel Estimator .............. 353
8.4.3 Comparison of the Slepian and Fourier Bases ....... 354
8.4.4 Krylov Approximation of the Reduced-Rank LMMSE
Channel Estimator ................................. 355
8.5 Linear Joint Antenna Multiuser Detection ................. 355
8.5.1 Multiuser Detection in Chip Space ................. 355
8.5.2 Multiuser Detection in User Space ................. 356
8.6 Nonlinear Detection ...................................... 358
8.6.1 Exploiting the Reduced-Rank Channel Model ......... 358
8.6.2 Soft Sphere Decoding .............................. 361
8.6.3 Computational Complexity .......................... 362
8.7 Simulation Results ....................................... 364
8.7.1 Bit Error Rate Comparison ......................... 364
8.7.2 Computational Complexity Comparison ............... 366
8.8 Conclusions .............................................. 368
Acknowledgments .......................................... 369
8.A Computation of the Log-Likelihood Ratio (8.44) ........... 369
References ............................................... 371
CHAPTER 9 Time-Scale and Dispersive Processing for Wideband
Time-Varying Channels ......................................... 375
9.1 Introduction ............................................. 375
9.1.1 Need for Wideband Channel Characterizations ....... 375
9.1.2 Examples of Wideband Dispersive Channel
Characteristics ................................... 377
9.1.3 Chapter Organization .............................. 380
9.2 Narrowband Channel Characterization ...................... 381
9.2.1 Narrowband Spreading Function ..................... 381
9.2.2 Discrete Channel Characterization and Finite
Approximations .................................... 381
9.3 Wideband Delay-Scale Channel Characterization ............ 383
9.3.1 Narrowband and Wideband Conditions ................ 383
9.3.2 Wideband Spreading Function ....................... 384
9.3.3 Discrete Delay-Scale Channel Characterization ..... 384
9.3.4 Finite Approximations ............................. 386
9.3.5 Multipath-Scale Diversity ......................... 387
9.3.6 Time-Scale Rake Receiver .......................... 389
9.4 Wideband Dispersive Channel Characterization ............. 392
9.4.1 Dispersive Time-Frequency Structures .............. 392
9.4.2 Dispersive Spreading Function and Unitary
Warping Relations ................................. 393
9.4.3 Discrete Dispersive Channel with Physical
Limitations ....................................... 394
9.4.4 Generalized Time-Frequency Rake Receiver .......... 395
9.5 Underwater Wireless Communication Channels ............... 396
9.5.1 Shallow Water Environment Model ................... 396
9.5.2 Time-Frequency Characteristics of Shallow Water
Environments ...................................... 398
9.5.3 Mode Separation in Time-Frequency ................. 398
9.5.4 Dispersion Diversity Receiver Design .............. 400
9.5.5 Numerical Simulations for Shallow Water
Communications .................................... 403
9.6 Application Example ...................................... 405
9.7 Conclusions .............................................. 410
References ............................................... 411
Index ......................................................... 417
|