Dedication .................................................... vii
Acknowledgments ................................................ ix
Preface ........................................................ xi
Changes from First Edition ..................................... xv
Changes from Second Edition ................................... xix
List of Figures .............................................. xxxi
Part 1. Elastic continua ........................................ 1
Introduction to Part 1 .......................................... 3
Chapter 1. Deformations ......................................... 7
Preliminary Remarks ............................................. 7
1.1 Notion of Continuum ........................................ 8
1.2 Rudiments of Continuum Mechanics .......................... 10
1.2.1 Axiomatic format ................................... 10
1.2.2 Primitive concepts of continuum mechanics .......... 11
1.3 Material and Spatial Descriptions ......................... 14
1.3.1 Fundamental concepts ............................... 14
1.3.2 Material time derivative ........................... 16
1.3.3 Conditions of linearized theory .................... 18
1.4 Strain .................................................... 23
1.4.1 Introductory comments .............................. 23
1.4.2 Derivation of strain tensor ........................ 23
1.4.3 Physical meaning of strain tensor .................. 27
1.5 Rotation Tensor and Rotation Vector ....................... 33
Closing Remarks ........................................... 34
1.6 Exercises ................................................. 35
Chapter 2. Forces and Balance Principles ....................... 43
Preliminary Remarks ....................................... 43
2.1 Conservation of Mass ...................................... 44
2.1.1 Introductory comments .............................. 44
2.1.2 Integral equation .................................. 44
2.1.3 Equation of continuity ............................. 46
2.2 Time Derivative of Volume Integral ........................ 47
2.3 Stress .................................................... 49
2.3.1 Stress as description of surface forces ............ 49
2.3.2 Traction ........................................... 50
2.4 Balance of Linear Momentum ................................ 51
2.5 Stress Tensor ............................................. 54
2.5.1 Traction on coordinate planes ...................... 54
2.5.2 Traction on arbitrary planes ....................... 56
2.6 Cauchy's Equations of Motion .............................. 61
2.6.1 General formulation ................................ 61
2.6.2 Surface-forces formulation ......................... 64
2.7 Balance of Angular Momentum ............................... 67
2.7.1 Introductory comments .............................. 67
2.7.2 Integral equation .................................. 69
2.7.3 Symmetry of stress tensor .......................... 70
2.8 Fundamental Equations ..................................... 74
Closing Remarks ........................................... 75
2.9 Exercises ................................................. 76
Chapter 3. Stress-Strain Equations ............................. 87
Preliminary Remarks ....................................... 87
3.1 Rudiments of Constitutive Equations ....................... 88
3.2 Formulation of Stress-Strain Equations: Hookean Solid ..... 90
3.2.1 Introductory comments .............................. 90
3.2.2 Tensor form ........................................ 91
3.2.3 Matrix form ........................................ 95
3.3 Determined System ......................................... 97
3.4 Anelasticity .............................................. 98
3.4.1 Introductory comments .............................. 98
3.4.2 Viscosity: Stokesian fluid ......................... 98
3.4.3 Viscoelasticity: Kelvin-Voigt model ................ 99
3.4.4 Viscoelasticity: Maxwell model .................... 104
Closing Remarks .......................................... 105
3.5 Exercises ................................................ 106
Chapter 4. Strain Energy ...................................... 113
Preliminary remarks ...................................... 113
4.1 Strain-energy Function ................................... 114
4.2 Strain-energy Function and Elasticity-tensor Symmetry .... 116
4.2.1 Fundamental considerations ........................ 116
4.2.2 Elasticity parameters ............................. 118
4.2.3 Matrix form of stress-strain equations ............ 118
4.2.4 Coordinate transformations ........................ 119
4.3 Stability Conditions ..................................... 120
4.3.1 Physical justification ............................ 120
4.3.2 Mathematical formulation .......................... 120
4.3.3 Constraints on elasticity parameters .............. 121
4.4 System of Equations for Elastic Continua ................. 122
4.4.1 Elastic continua .................................. 122
4.4.2 Governing equations ............................... 123
Closing Remarks .......................................... 125
4.5 Exercises ................................................ 126
Chapter 5. Material Symmetry ................................ 133
Preliminary remarks ...................................... 133
5.1 Orthogonal Transformations ............................... 134
5.1.1 Transformation matrix ............................. 134
5.1.2 Symmetry group .................................... 134
5.2 Transformation of Coordinates ............................ 135
5.2.1 Introductory comments ............................. 135
5.2.2 Transformation of stress-tensor components ........ 135
5.2.3 Transformation of strain-tensor components ........ 140
5.2.4 Stress-strain equations in transformed
coordinates ....................................... 141
5.2.5 On matrix forms ................................... 142
5.3 Condition for Material Symmetry .......................... 144
5.4 Point Symmetry ........................................... 147
5.5 Generally Anisotropic Continuum .......................... 148
5.6 Monoclinic Continuum ..................................... 149
5.6.1 Elasticity matrix ................................. 149
5.6.2 Vanishing of tensor components .................... 151
5.6.3 Natural coordinate system ......................... 152
5.7 Orthotropic Continuum .................................... 154
5.8 Trigonal Continuum ....................................... 157
5.8.1 Elasticity matrix ................................. 157
5.8.2 Natural coordinate system ......................... 158
5.9 Tetragonal Continuum ..................................... 159
5.9.1 Elasticity matrix ................................. 159
5.9.2 Natural coordinate system ......................... 161
5.10 Transversely Isotropic Continuum ......................... 162
5.10.1 Elasticity matrix ................................. 162
5.10.2 Rotation invariance ............................... 163
5.11 Cubic Continuum .......................................... 168
5.12 Isotropic Continuum ...................................... 170
5.12.1 Elasticity matrix ................................. 170
5.12.2 Lame's parameters ................................. 171
5.12.3 Tensor formulation ................................ 172
5.12.4 Physical meaning of Lame's parameters ............. 174
5.13 Relations Among Symmetry Classes ......................... 175
Closing Remarks .......................................... 177
5.14 Exercises ................................................ 178
Part 2. Waves and rays ........................................ 203
Introduction to Part 2 ................................... 205
Chapter 6. Equations of Motion: Isotropic Homogeneous
Continua ...................................................... 209
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 209
6.1 Wave Equations ........................................... 210
6.1.1 Equation of motion ................................ 210
6.1.2 Wave equation for P waves ......................... 213
6.1.3 Wave equation for S waves ......................... 214
6.1.4 Physical interpretation ........................... 216
6.2 Plane Waves .............................................. 217
6.3 Displacement Potentials .................................. 220
6.3.1 Helmholtz's decomposition ......................... 220
6.3.2 Gauge transformation .............................. 221
6.3.3 Equation of motion ................................ 222
6.3.4 P and S waves ..................................... 223
6.4 P and S Waves in Terms of Displacements .................. 226
6.5 Solutions of Wave Equation for Single Spatial Dimension .. 228
6.5.1 d'Alembert's approach ............................. 228
6.5.2 Directional derivative ............................ 234
6.5.3 Well-posed problem ................................ 235
6.5.4 Causality, finite propagation speed and
sharpness of signals .............................. 240
6.6 Solution of Wave Equation for Two and Three Spatial
Dimensions ............................................... 242
6.6.1 Introductory comments ............................. 242
6.6.2 Three spatial dimensions .......................... 243
6.6.3 Two spatial dimensions ............................ 245
6.7 On Evolution Equation .................................... 247
6.8 Solutions of Wave Equation for One-Dimensional
Scattering ............................................... 250
6.9 On Weak Solutions of Wave Equation ....................... 258
6.9.1 Introductory comments ............................. 258
6.9.2 Weak derivatives .................................. 260
6.9.3 Weak solution of wave equation .................... 260
6.10 Reduced Wave Equation .................................... 262
6.10.1 Harmonic-wave trial solution ...................... 262
6.10.2 Fourier's transform of wave equation .............. 264
6.11 Extensions of Wave Equation .............................. 266
6.11.1 Introductory comments ............................. 266
6.11.2 Standard wave equation ............................ 266
6.11.3 Wave equation and elliptical velocity dependence .. 267
6.11.4 Wave equation and weak inhomogeneity .............. 271
Closing Remarks .......................................... 278
6.12 Exercises ................................................ 279
Chapter 7. Equations of Motion: Anisotropic Inhomogeneous
Continua ...................................................... 307
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 307
7.1 Formulation of Equations ................................. 308
7.2 Formulation of Solutions ................................. 309
7.2.1 Introductory comments ............................. 309
7.2.2 Trial-solution formulation: General wave .......... 309
7.2.3 Trial-solution formulation: Harmonic wave ......... 312
7.2.4 Asymptotic-series formulation ..................... 315
7.3 Eikonal Equation ......................................... 321
Closing Remarks .......................................... 324
7.4 Exercises ................................................ 325
Chapter 8. Hamilton's Ray Equations ........................... 337
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 337
8.1 Method of Characteristics ................................ 338
8.1.1 Level-set functions ............................... 338
8.1.2 Characteristic equations .......................... 339
8.1.3 Consistency of formulation ........................ 343
8.2 Time Parametrization of Char ............................. 344
8.2.1 General formulation ............................... 344
8.2.2 Equations with variable scaling factor ............ 345
8.2.3 Equations with constant scaling factor ............ 346
8.2.4 Formulation of Hamilton's ray equations ........... 347
8.3 Physical Interpretation of Hamilton's Ray Equations
and Solutions ............................................ 348
8.3.1 Equations ......................................... 348
8.3.2 Solutions ......................................... 349
8.4 Relation between p and ẋ ................................. 350
8.4.1 General formulation ............................... 350
8.4.2 Phase and ray velocities .......................... 350
8.4.3 Phase and ray angles .............................. 353
8.4.4 Geometrical illustration .......................... 355
8.5 Example: Elliptical Anisotropy and Linear Inhomogeneity .. 356
8.5.1 Introductory comments ............................. 356
8.5.2 Eikonal equation .................................. 357
8.5.3 Hamilton's ray equations .......................... 359
8.5.4 Initial conditions ................................ 360
8.5.5 Physical interpretation of equations and
conditions ........................................ 360
8.5.6 Solution of Hamilton's ray equations .............. 362
8.5.7 Solution of eikonal equation ...................... 367
8.5.8 Physical interpretation of solutions .............. 368
8.6 Example: Isotropy and Inhomogeneity ...................... 368
8.6.1 Parametric form ................................... 368
8.6.2 Explicit form ..................................... 370
Closing Remarks .......................................... 371
8.7 Exercises ................................................ 372
Chapter 9. Christoffel's Equations ............................ 387
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 387
9.1 Explicit form of Christoffel's Equations ................. 388
9.2 Christoffel's Equations and Anisotropic Continua ......... 393
9.2.1 Introductory comments ............................. 393
9.2.2 Monoclinic continua ............................... 394
9.2.3 Transversely isotropic continua ................... 399
9.3 Phase-slowness Surfaces .................................. 407
9.3.1 Introductory comments ............................. 407
9.3.2 Convexity of innermost sheet ...................... 407
9.3.3 Intersection points ............................... 408
Closing Remarks .......................................... 411
9.4 Exercises ................................................ 411
Chapter 10. Reflection and Transmission ....................... 421
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 421
10.1 Angles at Interface ...................................... 422
10.1.1 Phase angles ...................................... 422
10.1.2 Ray angles ........................................ 424
10.1.3 Example: Elliptical velocity dependence ........... 425
10.2 Amplitudes at Interface .................................. 428
10.2.1 Kinematic and dynamic boundary conditions ......... 428
10.2.2 Reflection and transmission amplitudes ............ 434
Closing Remarks .......................................... 440
10.3 Exercises ................................................ 442
Chapter 11. Lagrange's Ray Equations ......................... 449
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 449
11.1 Legendre's Transformation of Hamiltonian ................. 450
11.2 Formulation of Lagrange's Ray Equations .................. 450
11.3 Beltrami's Identity ...................................... 453
Closing Remarks .......................................... 453
11.4 Exercises ................................................ 454
Part 3. Variational formulation of rays ....................... 459
Introduction to Part 3 ................................... 461
Chapter 12. Euler's Equations ................................ 465
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 465
12.1 Mathematical Background .................................. 466
12.2 Formulation of Euler's Equation .......................... 467
12.3 Beltrami's Identity ...................................... 470
12.4 Generalizations of Euler's Equation ...................... 471
12.4.1 Introductory comments ............................. 471
12.4.2 Case of several variables ......................... 471
12.4.3 Case of several functions ......................... 472
12.4.4 Higher-order derivatives .......................... 472
12.5 Special Cases of Euler's Equation ........................ 473
12.5.1 Introductory comments ............................. 473
12.5.2 Independence of z ................................. 474
12.5.3 Independence of x and z ........................... 474
12.5.4 Independence of x ................................. 475
12.5.5 Total derivative .................................. 475
12.5.6 Function of x and z ............................... 476
12.6 First Integrals .......................................... 479
12.7 Lagrange's Ray Equations as Euler's Equations ............ 480
Closing Remarks .......................................... 481
12.8 Exercises ................................................ 482
Chapter 13. Variational Principles ........................... 491
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 491
13.1 Fermat's Principle ....................................... 492
13.1.1 Statement of Fermat's principle ................... 492
13.1.2 Properties of Hamiltonian 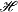 ...................... 493
13.1.3 Variational equivalent of Hamilton's ray
equations ......................................... 494
13.1.4 Properties of Lagrangian ...................... 493
13.1.3 Variational equivalent of Hamilton's ray
equations ......................................... 494
13.1.4 Properties of Lagrangian 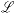 ....................... 494
13.1.5 Parameter-independent Lagrange's ray equations .... 497
13.1.6 Ray velocity ...................................... 498
13.1.7 Proof of Fermat's principle ....................... 498
13.2 Hamilton's Principle: Example ............................ 500
13.2.1 Introductory comments ............................. 500
13.2.2 Action ............................................ 500
13.2.3 Lagrange's equations of motion .................... 503
13.2.4 Wave equation ..................................... 505
Closing Remarks .......................................... 509
13.3 Exercises ................................................ 509
Chapter 14. Ray Parameters ................................... 519
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 519
14.1 Traveltime Integrals ..................................... 520
14.2 Ray Parameters as First Integrals ........................ 521
14.3 Example: Elliptical Anisotropy and Linear Inhomogeneity .. 522
14.3.1 Introductory comments ............................. 522
14.3.2 Rays .............................................. 523
14.3.3 Traveltimes ....................................... 526
14.4 Rays in Isotropic Continua ............................... 529
14.5 Lagrange's Ray Equations in xz-Plane ..................... 530
14.6 Conserved Quantities and Hamilton's Ray Equations ........ 531
Closing Remarks .......................................... 533
14.7 Exercises ................................................ 534
Part 4. Appendices ............................................ 545
Introduction to Part 4 ................................... 547
Appendix A. Euler's Homogeneous-Function Theorem ............. 549
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 549
A.l Homogeneous Functions .................................... 550
A.2 Homogeneous-Function Theorem ............................. 551
Closing Remarks .......................................... 553
Appendix В. Legendre's Transformation ........................ 555
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 555
B.l Geometrical Context ....................................... 556
В.1.1 Surface and its tangent planes .................... 556
B l.2 Single-variable case .............................. 556
B.2 Duality of Transformation ................................ 558
B.3 Transformation between Lagrangian ....................... 494
13.1.5 Parameter-independent Lagrange's ray equations .... 497
13.1.6 Ray velocity ...................................... 498
13.1.7 Proof of Fermat's principle ....................... 498
13.2 Hamilton's Principle: Example ............................ 500
13.2.1 Introductory comments ............................. 500
13.2.2 Action ............................................ 500
13.2.3 Lagrange's equations of motion .................... 503
13.2.4 Wave equation ..................................... 505
Closing Remarks .......................................... 509
13.3 Exercises ................................................ 509
Chapter 14. Ray Parameters ................................... 519
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 519
14.1 Traveltime Integrals ..................................... 520
14.2 Ray Parameters as First Integrals ........................ 521
14.3 Example: Elliptical Anisotropy and Linear Inhomogeneity .. 522
14.3.1 Introductory comments ............................. 522
14.3.2 Rays .............................................. 523
14.3.3 Traveltimes ....................................... 526
14.4 Rays in Isotropic Continua ............................... 529
14.5 Lagrange's Ray Equations in xz-Plane ..................... 530
14.6 Conserved Quantities and Hamilton's Ray Equations ........ 531
Closing Remarks .......................................... 533
14.7 Exercises ................................................ 534
Part 4. Appendices ............................................ 545
Introduction to Part 4 ................................... 547
Appendix A. Euler's Homogeneous-Function Theorem ............. 549
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 549
A.l Homogeneous Functions .................................... 550
A.2 Homogeneous-Function Theorem ............................. 551
Closing Remarks .......................................... 553
Appendix В. Legendre's Transformation ........................ 555
Preliminary Remarks ...................................... 555
B.l Geometrical Context ....................................... 556
В.1.1 Surface and its tangent planes .................... 556
B l.2 Single-variable case .............................. 556
B.2 Duality of Transformation ................................ 558
B.3 Transformation between Lagrangian 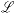 and Hamiltonian and Hamiltonian
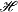 ....................................................... 559
B 4 Transformation and Ray Equations ......................... 560
Closing Remarks .......................................... 562
Appendix C. List of Symbols ................................... 563
C 1 Mathematical Relations and Operations .................... 563
C.2 Physical Quantities ...................................... 565
C 2.1 Greek letters ..................................... 565
C.2.2 Roman letters ..................................... 566
Bibliography .................................................. 567
Index ......................................................... 591
About the Author .............................................. 621 ....................................................... 559
B 4 Transformation and Ray Equations ......................... 560
Closing Remarks .......................................... 562
Appendix C. List of Symbols ................................... 563
C 1 Mathematical Relations and Operations .................... 563
C.2 Physical Quantities ...................................... 565
C 2.1 Greek letters ..................................... 565
C.2.2 Roman letters ..................................... 566
Bibliography .................................................. 567
Index ......................................................... 591
About the Author .............................................. 621
|