List of Symbols ................................................ xi
Acknowledgments .............................................. xiii
1 A Brief History .............................................. 1
1.1 Pre-1820: The Two Subjects of Electricity and
Magnetism ............................................... 1
1.2 1820-1861: The Experimental Glory Days of
Electricity and Magnetism ............................... 2
1.3 Maxwell and His Four Equations .......................... 2
1.4 Einstein and the Special Theory of Relativity ........... 2
1.5 Quantum Mechanics and Photons ........................... 3
1.6 Gauge Theories for Physicists: The Standard Model ....... 4
1.7 Four-Manifolds .......................................... 5
1.8 This Book ............................................... 7
1.9 Some Sources ............................................ 7
2 Maxwell's Equations .......................................... 9
2.1 A Statement of Maxwell's Equations ...................... 9
2.2 Other Versions of Maxwell's Equations .................. 12
2.2.1 Some Background in Nabla ........................ 12
2.2.2 Nabla and Maxwell ............................... 14
2.3 Exercises .............................................. 14
3 Electromagnetic Waves ....................................... 17
3.1 The Wave Equation ...................................... 17
3.2 Electromagnetic Waves .................................. 20
3.3 The Speed of Electromagnetic Waves Is Constant ......... 21
3.3.1 Intuitive Meaning ............................... 21
3.3.2 Changing Coordinates for the Wave Equation ...... 22
3.4 Exercises .............................................. 25
4 Special Relativity .......................................... 27
4.1 Special Theory of Relativity ........................... 27
4.2 Clocks and Rulers ...................................... 28
4.3 Galilean Transformations ............................... 31
4.4 Lorentz Transformations ................................ 32
4.4.1 A Heuristic Approach ............................ 32
4.4.2 Lorentz Contractions and Time Dilations ......... 35
4.4.3 Proper Time ..................................... 36
4.4.4 The Special Relativity Invariant ................ 37
4.4.5 Lorentz Transformations, the Minkowski Metric,
and Relativistic Displacement ................... 38
4.5 Velocity and Lorentz Transformations ................... 43
4.6 Acceleration and Lorentz Transformations ............... 45
4.7 Relativistic Momentum .................................. 46
4.8 Appendix: Relativistic Mass ............................ 48
4.8.1 Mass and Lorentz Transformations ................ 48
4.8.2 More General Changes in Mass .................... 51
4.9 Exercises .............................................. 52
5 Mechanics and Maxwell's Equations ........................... 56
5.1 Newton's Three Laws .................................... 56
5.2 Forces for Electricity and Magnetism ................... 58
5.2.1 F = q(E + v × B) ................................ 58
5.2.2 Coulomb's Law ................................... 59
5.3 Force and Special Relativity ........................... 60
5.3.1 The Special Relativistic Force .................. 60
5.3.2 Force and Lorentz Transformations ............... 61
5.4 Coulomb + Special Relativity + Charge Conservation =
Magnetism .............................................. 62
5.5 Exercises .............................................. 65
6 Mechanics, Lagrangians, and the Calculus of Variations ...... 70
6.1 Overview of Lagrangians and Mechanics .................. 70
6.2 Calculus of Variations ................................. 71
6.2.1 Basic Framework ................................. 71
6.2.2 Euler-Lagrange Equations ........................ 73
6.2.3 More Generalized Calculus of Variations
Problems ........................................ 77
6.3 A Lagrangian Approach to Newtonian Mechanics ........... 78
6.4 Conservation of Energy from Lagrangians ................ 83
6.5 Noether's Theorem and Conservation Laws ................ 85
6.6 Exercises .............................................. 86
7 Potentials .................................................. 88
7.1 Using Potentials to Create Solutions for Maxwell's
Equations .............................................. 88
7.2 Existence of Potentials ................................ 89
7.3 Ambiguity in the Potential ............................. 91
7.4 Appendix: Some Vector Calculus ......................... 91
7.5 Exercises .............................................. 95
8 Lagrangians and Electromagnetic Forces ...................... 98
8.1 Desired Properties for the Electromagnetic Lagrangian .. 98
8.2 The Electromagnetic Lagrangian ......................... 99
8.3 Exercises ............................................. 101
9 Differential Forms ......................................... 103
9.1 The Vector Spaces Λk(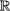 n) .............................. 103
9.1.1 A First Pass at the Definition ................. 103
9.1.2 Functions as Coefficients ...................... 106
9.1.3 The Exterior Derivative ........................ 106
9.2 Tools for Measuring ................................... 109
9.2.1 Curves in n) .............................. 103
9.1.1 A First Pass at the Definition ................. 103
9.1.2 Functions as Coefficients ...................... 106
9.1.3 The Exterior Derivative ........................ 106
9.2 Tools for Measuring ................................... 109
9.2.1 Curves in 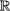 3 ................................... 109
9.2.2 Surfaces in 3 ................................... 109
9.2.2 Surfaces in 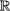 3 ................................. 111
9.2.3 k-manifolds in 3 ................................. 111
9.2.3 k-manifolds in 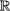 n .............................. 113
9.3 Exercises ............................................. 115
10 The Hodge *Operator ........................................ 119
10.1 The Exterior Algebra and the * Operator ............... 119
10.2 Vector Fields and Differential Forms .................. 121
10.3 The ? Operator and Inner Products ..................... 122
10.4 Inner Products on Λ( n .............................. 113
9.3 Exercises ............................................. 115
10 The Hodge *Operator ........................................ 119
10.1 The Exterior Algebra and the * Operator ............... 119
10.2 Vector Fields and Differential Forms .................. 121
10.3 The ? Operator and Inner Products ..................... 122
10.4 Inner Products on Λ(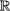 n) ............................... 123
10.5 The * Operator with the Minkowski Metric .............. 125
10.6 Exercises ............................................. 127
11 The Electromagnetic Two-Form ............................... 130
11.1 The Electromagnetic Two-Form .......................... 130
11.2 Maxwell's Equations via Forms ......................... 130
11.3 Potentials ............................................ 131
11.4 Maxwell's Equations via Lagrangians ................... 132
11.5 Euler-Lagrange Equations for the Electromagnetic
Lagrangian ............................................ 136
11.6 Exercises ............................................. 139
12 Some Mathematics Needed for Quantum Mechanics .............. 142
12.1 Hilbert Spaces ........................................ 142
12.2 Hermitian Operators ................................... 149
12.3 The Schwartz Space .................................... 153
12.3.1 The Definition ................................. 153
12.3.2 The Operators q(ƒ) = xƒ and p(ƒ) = -idƒ/dx ..... 155
12.3.3 S( n) ............................... 123
10.5 The * Operator with the Minkowski Metric .............. 125
10.6 Exercises ............................................. 127
11 The Electromagnetic Two-Form ............................... 130
11.1 The Electromagnetic Two-Form .......................... 130
11.2 Maxwell's Equations via Forms ......................... 130
11.3 Potentials ............................................ 131
11.4 Maxwell's Equations via Lagrangians ................... 132
11.5 Euler-Lagrange Equations for the Electromagnetic
Lagrangian ............................................ 136
11.6 Exercises ............................................. 139
12 Some Mathematics Needed for Quantum Mechanics .............. 142
12.1 Hilbert Spaces ........................................ 142
12.2 Hermitian Operators ................................... 149
12.3 The Schwartz Space .................................... 153
12.3.1 The Definition ................................. 153
12.3.2 The Operators q(ƒ) = xƒ and p(ƒ) = -idƒ/dx ..... 155
12.3.3 S(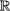 ) Is Not a Hilbert Space .................... 157
12.4 Caveats: On Lebesgue Measure, Types of Convergence,
and Different Bases ................................... 159
12.5 Exercises ............................................. 160
13 Some Quantum Mechanical Thinking ........................... 163
13.1 The Photoelectric Effect: Light as Photons ............ 163
13.2 Some Rules for Quantum Mechanics ...................... 164
13.3 Quantization .......................................... 170
13.4 Warnings of Subtleties ................................ 172
13.5 Exercises ............................................. 172
14 Quantum Mechanics of Harmonic Oscillators .................. 176
14.1 The Classical Harmonic Oscillator ..................... 176
14.2 The Quantum Harmonic Oscillator ....................... 179
14.3 Exercises ............................................. 184
15 Quantizing Maxwell's Equations ............................. 186
15.1 Our Approach .......................................... 186
15.2 The Coulomb Gauge ..................................... 187
15.3 The "Hidden" Harmonic Oscillator ...................... 193
15.4 Quantization of Maxwell's Equations ................... 195
15.5 Exercises ............................................. 197
16 Manifolds .................................................. 201
16.1 Introduction to Manifolds ............................. 201
16.1.1 Force = Curvature ................................... 201
16.1.2 Intuitions behind Manifolds ......................... 201
16.2 Manifolds Embedded in ) Is Not a Hilbert Space .................... 157
12.4 Caveats: On Lebesgue Measure, Types of Convergence,
and Different Bases ................................... 159
12.5 Exercises ............................................. 160
13 Some Quantum Mechanical Thinking ........................... 163
13.1 The Photoelectric Effect: Light as Photons ............ 163
13.2 Some Rules for Quantum Mechanics ...................... 164
13.3 Quantization .......................................... 170
13.4 Warnings of Subtleties ................................ 172
13.5 Exercises ............................................. 172
14 Quantum Mechanics of Harmonic Oscillators .................. 176
14.1 The Classical Harmonic Oscillator ..................... 176
14.2 The Quantum Harmonic Oscillator ....................... 179
14.3 Exercises ............................................. 184
15 Quantizing Maxwell's Equations ............................. 186
15.1 Our Approach .......................................... 186
15.2 The Coulomb Gauge ..................................... 187
15.3 The "Hidden" Harmonic Oscillator ...................... 193
15.4 Quantization of Maxwell's Equations ................... 195
15.5 Exercises ............................................. 197
16 Manifolds .................................................. 201
16.1 Introduction to Manifolds ............................. 201
16.1.1 Force = Curvature ................................... 201
16.1.2 Intuitions behind Manifolds ......................... 201
16.2 Manifolds Embedded in 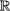 n .............................. 203
16.2.1 Parametric Manifolds ................................ 203
16.2.2 Implicitly Defined Manifolds ........................ 205
16.3 Abstract Manifolds .................................... 206
16.3.1 Definition .......................................... 206
16.3.2 Functions on a Manifold ............................. 212
16.4 Exercises ............................................. 212
17 Vector Bundles ............................................. 214
17.1 Intuitions ............................................ 214
17.2 Technical Definitions ................................. 216
17.2.1 The Vector Space n .............................. 203
16.2.1 Parametric Manifolds ................................ 203
16.2.2 Implicitly Defined Manifolds ........................ 205
16.3 Abstract Manifolds .................................... 206
16.3.1 Definition .......................................... 206
16.3.2 Functions on a Manifold ............................. 212
16.4 Exercises ............................................. 212
17 Vector Bundles ............................................. 214
17.1 Intuitions ............................................ 214
17.2 Technical Definitions ................................. 216
17.2.1 The Vector Space 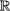 k ............................ 216
17.2.2 Definition of a Vector Bundle .................. 216
17.3 Principal Bundles ..................................... 219
17.4 Cylinders and Mцbius Strips ........................... 220
17.5 Tangent Bundles ....................................... 222
17.5.1 Intuitions ..................................... 222
17.5.2 Tangent Bundles for Parametrically Defined
Manifolds ...................................... 224
17.5.3 T( k ............................ 216
17.2.2 Definition of a Vector Bundle .................. 216
17.3 Principal Bundles ..................................... 219
17.4 Cylinders and Mцbius Strips ........................... 220
17.5 Tangent Bundles ....................................... 222
17.5.1 Intuitions ..................................... 222
17.5.2 Tangent Bundles for Parametrically Defined
Manifolds ...................................... 224
17.5.3 T( 2) as Partial Derivatives ................... 225
17.5.4 Tangent Space at a Point of an Abstract
Manifold ....................................... 227
17.5.5 Tangent Bundles for Abstract Manifolds ......... 228
17.6 Exercises ............................................. 230
18 Connections ................................................ 232
18.1 Intuitions ............................................ 232
18.2 Technical Definitions ................................. 233
18.2.1 Operator Approach .............................. 233
18.2.2 Connections for Trivial Bundles ................ 237
18.3 Covariant Derivatives of Sections ..................... 240
18.4 Parallel Transport: Why Connections Are Called
Connections ........................................... 243
18.5 Appendix: Tensor Products of Vector Spaces ............ 247
18.5.1 A Concrete Description ......................... 247
18.5.2 Alternating Forms as Tensors ................... 248
18.5.3 Homogeneous Polynomials as Symmetric Tensors ... 250
18.5.4 Tensors as Linearizations of Bilinear Maps ..... 251
18.6 Exercises ............................................. 253
19 Curvature .................................................. 257
19.1 Motivation ............................................ 257
19.2 Curvature and the Curvature Matrix .................... 258
19.3 Deriving the Curvature Matrix ......................... 260
19.4 Exercises ............................................. 261
20 Maxwell via Connections and Curvature ...................... 263
20.1 Maxwell in Some of Its Guises ......................... 263
20.2 Maxwell for Connections and Curvature ................. 264
20.3 Exercises ............................................. 266
20.1 21 The Lagrangian Machine, Yang-Mills, and Other
Forces ................................................ 267
21.1 The Lagrangian Machine ................................ 267
21.2 U(l) Bundles .......................................... 268
21.3 Other Forces .......................................... 269
21.4 A Dictionary .......................................... 270
21.5 Yang-Mills Equations .................................. 272
Bibliography .................................................. 275
Index ......................................................... 279
Color plates follow ........................................... 234 2) as Partial Derivatives ................... 225
17.5.4 Tangent Space at a Point of an Abstract
Manifold ....................................... 227
17.5.5 Tangent Bundles for Abstract Manifolds ......... 228
17.6 Exercises ............................................. 230
18 Connections ................................................ 232
18.1 Intuitions ............................................ 232
18.2 Technical Definitions ................................. 233
18.2.1 Operator Approach .............................. 233
18.2.2 Connections for Trivial Bundles ................ 237
18.3 Covariant Derivatives of Sections ..................... 240
18.4 Parallel Transport: Why Connections Are Called
Connections ........................................... 243
18.5 Appendix: Tensor Products of Vector Spaces ............ 247
18.5.1 A Concrete Description ......................... 247
18.5.2 Alternating Forms as Tensors ................... 248
18.5.3 Homogeneous Polynomials as Symmetric Tensors ... 250
18.5.4 Tensors as Linearizations of Bilinear Maps ..... 251
18.6 Exercises ............................................. 253
19 Curvature .................................................. 257
19.1 Motivation ............................................ 257
19.2 Curvature and the Curvature Matrix .................... 258
19.3 Deriving the Curvature Matrix ......................... 260
19.4 Exercises ............................................. 261
20 Maxwell via Connections and Curvature ...................... 263
20.1 Maxwell in Some of Its Guises ......................... 263
20.2 Maxwell for Connections and Curvature ................. 264
20.3 Exercises ............................................. 266
20.1 21 The Lagrangian Machine, Yang-Mills, and Other
Forces ................................................ 267
21.1 The Lagrangian Machine ................................ 267
21.2 U(l) Bundles .......................................... 268
21.3 Other Forces .......................................... 269
21.4 A Dictionary .......................................... 270
21.5 Yang-Mills Equations .................................. 272
Bibliography .................................................. 275
Index ......................................................... 279
Color plates follow ........................................... 234
|