Preface ....................................................... vii
List of Symbols ................................................ xi
1 Introduction ................................................. 1
1.1 Motivation .............................................. 1
1.2 Paradox: Does quantum mechanics tacitly imply that
0=1? .................................................... 5
1.3 Guiding the reader through this book .................... 6
2 Introduction to Groups ....................................... 9
2.1 Definition .............................................. 9
2.2 Remarks on axioms ...................................... 10
2.3 Examples ............................................... 11
2.4 Subgroups .............................................. 20
2.5 Homomorphism ........................................... 20
2.6 Equivalence classes .................................... 21
2.7 The assets of abstraction .............................. 22
2.8 Intuition and rigour ................................... 24
2.9 Symmetry ............................................... 25
2.10 Wave-like eigenfunctions ............................... 32
2.11 Group representations .................................. 40
2.12 Reducible and irreducible representations .............. 40
2.13 Eigenvector spaces ..................................... 42
2.14 Groups and physics — final remarks ..................... 45
3 Spinors in the Rotation Group ............................... 47
3.1 Preamble ............................................... 47
3.2 Tensor products ........................................ 48
3.3 What is a spinor or what kind of thing does a matrix
of SU(2) work on? ...................................... 48
3.4 Why we need a "Vielbein" ............................... 52
3.5 Dirac's method to code 3D vectors as 2D complex
quantities ............................................. 56
3.6 From vectors to spinors: Preliminary description ....... 59
3.7 From vectors to spinors: Detailed derivation
of the expression of the spinors ....................... 60
3.8 A treatment based on the stereographic projection
as a source of confusion ............................... 63
3.9 Harmonic polynomials ................................... 67
3.10 A very important isomorphism within representations
based on harmonic polynomials .......................... 71
3.11 Important consequences for quantum mechanics ........... 72
4 Spinors in the Homogeneous Lorentz Group .................... 93
4.1 It takes two different zero-length vectors to code
the whole tetrad ....................................... 93
4.2 The representations SL(2,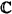 ) ............................ 96
4.3 Dirac's expedient again ................................ 96
4.4 Coding a tetrad in SL(2, ) ............................ 96
4.3 Dirac's expedient again ................................ 96
4.4 Coding a tetrad in SL(2,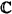 ) using tensor products
that involve the two semi-spinors ...................... 99
4.5 A very important difference between SL(2, ) using tensor products
that involve the two semi-spinors ...................... 99
4.5 A very important difference between SL(2,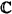 ) and
SU(2) ................................................. 100
4.6 The two types of zero-length vectors in the
Lorentz group that define a tetrad .................... 102
4.7 Dotted spinors ........................................ 104
4.8 Missing phase factors or boost parameters ............. 106
4.9 The coding of the tetrad in the Dirac representation .. 106
4.10 The last parameter in any group SO(ni,7i2) is always
a "phase factor" ...................................... 109
4.11 Expressing the tetrad in terms of more physical
parameters ............................................ 110
4.12 Final considerations .................................. 110
5 The Dirac Equation from Scratch ............................ 113
5.1 The Dirac equation in free space — first approach ..... 113
5.2 A warning about the superposition principle and the
negative energies ..................................... 124
5.3 Guidance through the rest of this chapter ............. 125
5.4 Spin and the group ring ............................... 129
5.5 Fully deterministic free-space Dirac-like equation:
Exact derivation of the Dirac equation ................ 150
5.6 The Dirac equation in the presence of an
electromagnetic potential ............................. 176
5.7 The g-factor of the electron .......................... 180
5.8 More over-interpretations in traditional quantum
mechanics ............................................. 184
5.9 Conclusion ............................................ 185
5.10 Complementary remarks on mathematics .................. 185
6 Towards a Better Understanding of Quantum Mechanics ........ 199
6.1 The phase velocity of the de Broglie wave ............. 199
6.2 Quantization as a pure consequence of Lorentz
invariance ............................................ 204
6.3 Probabilities and many histories ...................... 247
6.4 Further support for the "all-histories" approach ...... 249
6.5 Final remark .......................................... 250
7 The Hidden-Variables Issue and the Bell Inequalities ....... 253
7.1 Is our approach a hidden variables theory? ............ 253
7.2 The Bell inequalities ................................. 254
7.3 Several types of "independence" ....................... 256
7.4 Gedankenexperiment with snooker balls ................. 258
7.5 The Bell inequalities without any assumption about
locality .............................................. 263
7.6 Second Gedankenexperiment ............................. 267
7.7 Conclusion ............................................ 277
8 Equivalence of the Bohr-Sommerfeld and Dirac Theories for
the Hydrogen Atom .......................................... 281
8.1 Introduction .......................................... 281
8.2 Quantization of the Coulomb problem — first approach .. 281
9 The Problem of the Electron Spin within a Magnetic Field ... 297
9.1 Landau levels in a magnetic field ..................... 297
9.2 Traditional description of the spin in a magnetic
field ................................................. 300
9.3 Problems with the traditional treatment of spin
dynamics .............................................. 304
9.4 Describing precession of a single particle ............ 310
9.5 Solution to the conceptual problems associated
with misaligned spin .................................. 317
9.6 What is the coupling of the spin to the magnetic
field? ................................................ 322
10 The Double-Slit Experiment and the Superposition
Principle .................................................. 327
10.1 An approach inspired by the treatment of the
Aharonov-Bohm effect .................................. 327
11 A Caveat About the Limitations of Group Theory ............. 337
11.1 A same group-theoretical formalism can represent
several, very different physical mechanisms ........... 337
12 Spin and Angular Momentum as Vector and Bi-Vector
Concepts ................................................... 341
12.1 Lorentz covariance of bi-vectors ..................... 341
12.2 An inconvenient truth ................................ 344
Appendix A Discovering SL(2,C) Starting from the Cartan
Representation ............................................. 347
Appendix В Differences in the Spinor Formalisms Between
SO(3) and SL(2,C) .......................................... 349
Appendix С Additional Results on the Lorentz Group ............ 353
C.l General form of an element of the Lorentz group ....... 353
C.2 Coding of a general Lorentz transformation: Boost
and rotation parameters ............................... 354
C.3 Decoding of a general Lorentz transformation: Boost
and rotation parameters ............................... 355
C.4 Decoding of a general Lorentz transformation:
Coordinates of the tetrad ............................. 357
С.5 The electromagnetic field and angular momentum
as a tensor quantities ................................ 358
Appendix D The Analogy Between Electromagnetism and
Gravitation ................................................ 365
D.l Influence of the potential on the rest mass ........... 365
D.2 Polarization effects .................................. 369
Bibliography .................................................. 371
Index ......................................................... 375 ) and
SU(2) ................................................. 100
4.6 The two types of zero-length vectors in the
Lorentz group that define a tetrad .................... 102
4.7 Dotted spinors ........................................ 104
4.8 Missing phase factors or boost parameters ............. 106
4.9 The coding of the tetrad in the Dirac representation .. 106
4.10 The last parameter in any group SO(ni,7i2) is always
a "phase factor" ...................................... 109
4.11 Expressing the tetrad in terms of more physical
parameters ............................................ 110
4.12 Final considerations .................................. 110
5 The Dirac Equation from Scratch ............................ 113
5.1 The Dirac equation in free space — first approach ..... 113
5.2 A warning about the superposition principle and the
negative energies ..................................... 124
5.3 Guidance through the rest of this chapter ............. 125
5.4 Spin and the group ring ............................... 129
5.5 Fully deterministic free-space Dirac-like equation:
Exact derivation of the Dirac equation ................ 150
5.6 The Dirac equation in the presence of an
electromagnetic potential ............................. 176
5.7 The g-factor of the electron .......................... 180
5.8 More over-interpretations in traditional quantum
mechanics ............................................. 184
5.9 Conclusion ............................................ 185
5.10 Complementary remarks on mathematics .................. 185
6 Towards a Better Understanding of Quantum Mechanics ........ 199
6.1 The phase velocity of the de Broglie wave ............. 199
6.2 Quantization as a pure consequence of Lorentz
invariance ............................................ 204
6.3 Probabilities and many histories ...................... 247
6.4 Further support for the "all-histories" approach ...... 249
6.5 Final remark .......................................... 250
7 The Hidden-Variables Issue and the Bell Inequalities ....... 253
7.1 Is our approach a hidden variables theory? ............ 253
7.2 The Bell inequalities ................................. 254
7.3 Several types of "independence" ....................... 256
7.4 Gedankenexperiment with snooker balls ................. 258
7.5 The Bell inequalities without any assumption about
locality .............................................. 263
7.6 Second Gedankenexperiment ............................. 267
7.7 Conclusion ............................................ 277
8 Equivalence of the Bohr-Sommerfeld and Dirac Theories for
the Hydrogen Atom .......................................... 281
8.1 Introduction .......................................... 281
8.2 Quantization of the Coulomb problem — first approach .. 281
9 The Problem of the Electron Spin within a Magnetic Field ... 297
9.1 Landau levels in a magnetic field ..................... 297
9.2 Traditional description of the spin in a magnetic
field ................................................. 300
9.3 Problems with the traditional treatment of spin
dynamics .............................................. 304
9.4 Describing precession of a single particle ............ 310
9.5 Solution to the conceptual problems associated
with misaligned spin .................................. 317
9.6 What is the coupling of the spin to the magnetic
field? ................................................ 322
10 The Double-Slit Experiment and the Superposition
Principle .................................................. 327
10.1 An approach inspired by the treatment of the
Aharonov-Bohm effect .................................. 327
11 A Caveat About the Limitations of Group Theory ............. 337
11.1 A same group-theoretical formalism can represent
several, very different physical mechanisms ........... 337
12 Spin and Angular Momentum as Vector and Bi-Vector
Concepts ................................................... 341
12.1 Lorentz covariance of bi-vectors ..................... 341
12.2 An inconvenient truth ................................ 344
Appendix A Discovering SL(2,C) Starting from the Cartan
Representation ............................................. 347
Appendix В Differences in the Spinor Formalisms Between
SO(3) and SL(2,C) .......................................... 349
Appendix С Additional Results on the Lorentz Group ............ 353
C.l General form of an element of the Lorentz group ....... 353
C.2 Coding of a general Lorentz transformation: Boost
and rotation parameters ............................... 354
C.3 Decoding of a general Lorentz transformation: Boost
and rotation parameters ............................... 355
C.4 Decoding of a general Lorentz transformation:
Coordinates of the tetrad ............................. 357
С.5 The electromagnetic field and angular momentum
as a tensor quantities ................................ 358
Appendix D The Analogy Between Electromagnetism and
Gravitation ................................................ 365
D.l Influence of the potential on the rest mass ........... 365
D.2 Polarization effects .................................. 369
Bibliography .................................................. 371
Index ......................................................... 375
|